https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-025-06463-1
Regular Article
Ag-doped hematite/rGO nanocomposites for effective methylene blue dye degradation: study of structural, optical and chemical properties
1
Nano Research Laboratory, Department of Physics, DAV University, 144012, Jalandhar, Punjab, India
2
School of Bioengineering and Biosciences, Lovely Professional University, 144411, Jalandhar, Punjab, India
3
Department of Physics and Astronomical Sciences, Central University of Jammu, J&K, 181143, Samba, India
Received:
4
January
2025
Accepted:
22
May
2025
Published online:
12
June
2025
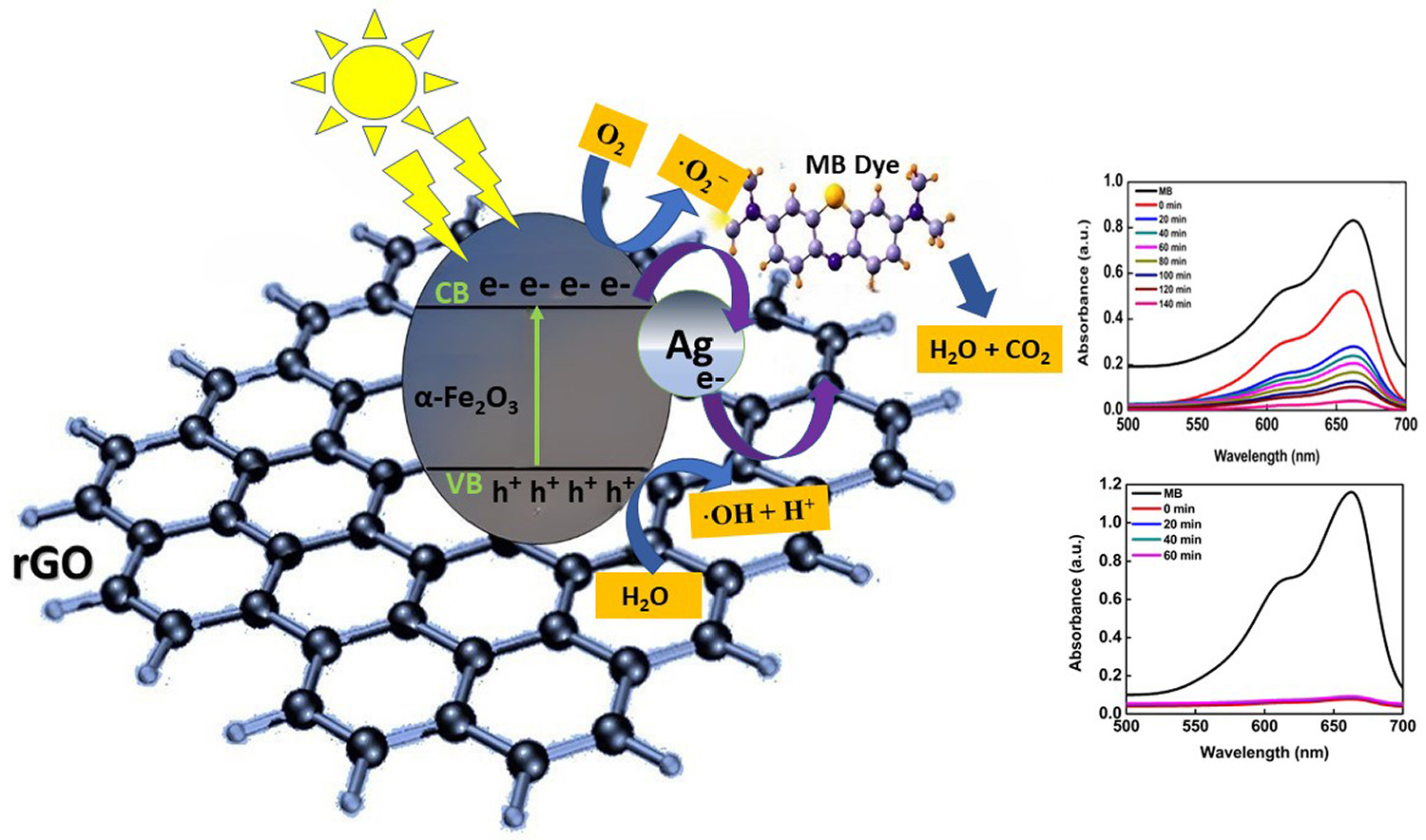
In this study, silver-doped α-Fe2O3/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites with varying graphene oxide concentrations were synthesized using a co-precipitation method followed by annealing. The resulting nanocomposites were extensively analyzed to investigate their structural, optical, and chemical properties. The absence of the rGO stacking peak at ~ 26° in XRD patterns indicates the distribution of rGO on hematite nanocrystals. Crystallite size analysis, performed using the Debye–Scherrer formula, reveals sizes ranging over 20.3–23.3 nm for the hematite in the nanocomposite samples. The diffraction peaks (111) and (200) planes of metallic silver (Ag°) cluster of crystallite size (5–6 nm) were obtained, along with the peaks of hematite phase. The morphology and particle size distribution of the Ag-doped α-Fe2O3/rGO nanocomposite were analysed using FESEM and the average particle size was about 29.5 nm. FTIR spectra reveal Fe–O stretching peaks and confirm successful reduction of GO. A significant increase in intensity of the D and G bands in Raman spectra with increasing GO might be due to surface plasmon resonance of silver clustering. A positive binding energy shift in the XPS core level spectra Fe2p of the nanocomposite sample confirmed the interaction of Ag-doped hematite with rGO. XPS analysis revealed Ag+ incorporation into the hematite lattice and Ag° clustering was about 0.08 and 0.14 at.%, respectively. Dye degradation efficiency of nanocomposite samples was tested by methylene blue dye adsorption and photocatalysis under solar irradiation at the catalyst loads of 0.2 and 0.9 g/L with the dye concentrations of 5 µM and 10 µM, respectively.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2025
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.