https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-025-06434-6
Regular Article
Gravimetric, electrochemical, surface morphological, and simulation studies of the use of expired Meftal-P drug as a novel anti-corrosive coating material for steel in 0.5 M HCl
1
Department of Chemistry, Chandigarh University Gharuan Mohali, Ludhiana Chandigarh National Highway NH-05, 140413, Ludhiana, India
2
Queensland Micro and Nanotechnology Centre, Griffith University, 4111, Nathan, QLD, Australia
3
Department of VLSI Microelectronics, Saveetha School of Engineering, Saveetha Institute of Medical and Technical Sciences (SIMATS), Saveetha University, 602105, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
4
Environmental and Atmospheric Sciences Research Group, Scientific Research Center, Al-Ayen University, 64001, Nasiriyah, Thi-Qar, Iraq
5
Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, College of Pharmacy, King Saud University, P.O. Box 2457, 11451, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
6
National Research Nuclear University “MEPhI”, Kashirskoe Shosse 31, 115409, Moscow, Russian Federation
7
Chemical & Materials Engineering, New Uzbekistan University, 54 Mustaqillik Ave, 100007, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
8
Faculty of Chemistry, National University of Uzbekistan, 100034, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
9
Physics and Chemistry, Western Caspian University, AZ-1001, Baku, Azerbaijan
10
Department of Chemistry, Government Digvijay Autonomous Postgraduate College, 491441, Rajnandgaon, Chhattisgarh, India
Received:
19
January
2025
Accepted:
13
May
2025
Published online:
2
June
2025
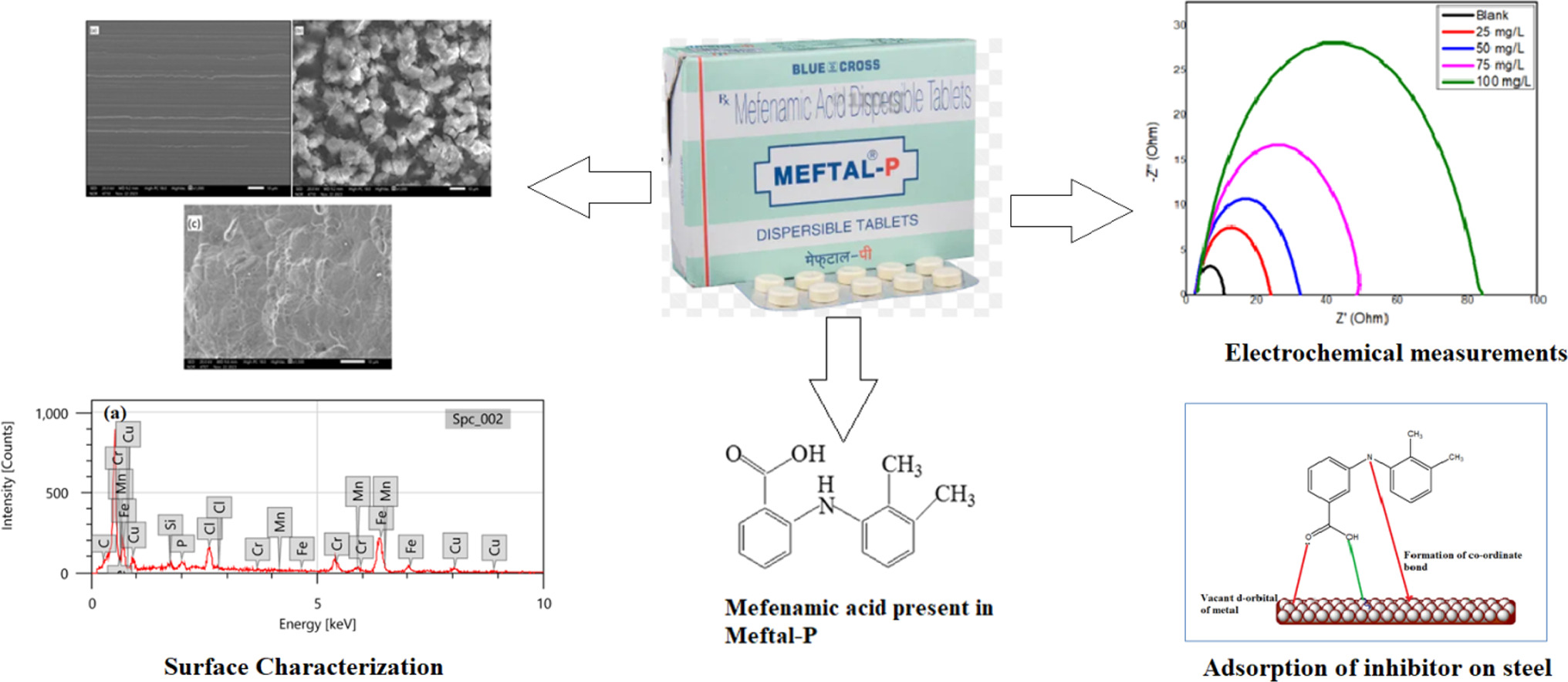
This study explores the novel but potentially effective first-time use of the expired Meftal-P drug, an anti-inflammatory drug, as a pickling agent that can reduce steel corrosion. The study is a sustainable and cost-effective approach to repurposing pharmaceutical waste. The objective of this study is to meet the need for corrosion mitigation strategies while simultaneously recycling pharmaceutical waste for beneficial uses. The study uses a range of analytical approaches, including weight loss, electrochemical methods, SEM–EDS, and simulation studies to assess how well the Meftal-P drug inhibits steel corrosion in 0.5 M HCl solution. The study’s findings report a remarkable inhibition efficiency of 95.83% at 100 mg/L concentration of the Meftal-P drug. SEM examination confirms the presence of a persistent Meftal-P inhibitor layer on the steel surface, demonstrating its corrosion inhibition characteristics. Further various adsorption isotherm models were fitted with data out of which the Langmuir adsorption isotherm is the best-fitted model with R2 value of 0.996. DFT analysis of the Meftal-P drug reveals the donor–acceptor mechanism between the metal and inhibitor.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2025
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.