https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-025-06355-4
Regular Article
Transmission dynamics of rabies through stochastic analysis with the effect of vaccination in dogs population
1
Department of Pharmacy, Abasyn University, 25000, Peshawar, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan
2
Nursing Department, Fatima College of Health Sciences, Madinat Zayed, UAE
3
Faculty of Nursing, Ain Shams University, Cairo, Egypt
4
Department of Nursing Management and Education, College of Nursing, Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
5
Department of Computational Mathematics and Computer Science, Institute of Natural Sciences and Mathematics, Ural Federal University, 19 Mira St., 620002, Yekaterinburg, Russia
6
Department of Mechanics and Mathematics, Western Caspian University, 1001, Baku, Azerbaijan
Received:
22
February
2025
Accepted:
22
April
2025
Published online:
26
May
2025
Each year, approximately 55,000 people die from the rabies virus, which is transmitted by dogs. Since deterministic approaches ignore effect randomness, such as different environmental factors that affect the rabies process dynamics. In this study, the stochastic epidemic model with the impact of vaccination for dogs is considered to investigate the transmission dynamics of rabies in the population with white noise effect. Firstly, we demonstrate the existence of a global solution and its positive impact. The basic stochastic reproduction number is then computed as a threshold that determines the persistence or extinction of the disease. If 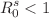 then the disease will be extinct from the population. And if
then the disease will be extinct from the population. And if 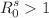 the disease continues to persist in the population. Finally, we perform the numerical simulation to examine the impact of various parameters on the propagation of disease. The numerical simulation shows that vaccination plays a critical role in the control of the disease. In contrast, the disease spreads when infected dogs met susceptible humans and dogs.
the disease continues to persist in the population. Finally, we perform the numerical simulation to examine the impact of various parameters on the propagation of disease. The numerical simulation shows that vaccination plays a critical role in the control of the disease. In contrast, the disease spreads when infected dogs met susceptible humans and dogs.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2025
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




