https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-025-06292-2
Regular Article
Modulational instability and kink, anti-kink, breather soliton for nonlocal reverse space time dispersive nonlinear Schrödinger equation
1
Department of Physics, School of Advanced Sciences, Vellore Institute of Technology, Chennai Campus, Kelampakkam Road, 600127, Chennai, Tamilnadu, India
2
Department of Physics, University College of Engineering, Anna University, 623513, Ramanathapuram, Tamilnadu, India
3
Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Science, Cairo University, 12613, Giza, Egypt
Received:
29
November
2024
Accepted:
2
April
2025
Published online:
30
April
2025
In this paper, we examine the soliton solutions of a new form of the nonlocal reverse space time dispersive nonlinear Schrödinger equation which describes the propagation of solitons in optical fiber. We also aim to understand the role of higher-order dispersion in the dynamics of solitons in optical fibers. Hence, the proposed equation is solved with the help of 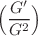 -expansion method, and some novel solutions are presented for local and nonlocal field. The role of higher-order dispersion on the dynamics of the soliton in optical fiber is discussed both in the absence and in the presence of nonlinear dispersion. We analyze the physical parameters responsible for the evolution of local and nonlocal soliton solutions in optical fiber. We also explore the stability of solutions of dynamical equation using linear stability analysis. The stability of the soliton solutions is presented using the modulational instability gain, and the role of physical parameters on the stability of solutions is also discussed.
-expansion method, and some novel solutions are presented for local and nonlocal field. The role of higher-order dispersion on the dynamics of the soliton in optical fiber is discussed both in the absence and in the presence of nonlinear dispersion. We analyze the physical parameters responsible for the evolution of local and nonlocal soliton solutions in optical fiber. We also explore the stability of solutions of dynamical equation using linear stability analysis. The stability of the soliton solutions is presented using the modulational instability gain, and the role of physical parameters on the stability of solutions is also discussed.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2025
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




