https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-025-06241-z
Regular Article
Black hole with global monopole charge in self-interacting Kalb-Ramond field
1
Centro de Investigación en Ciencias del Espacio y Física Teórica, Universidad Central de Chile, 1710164, La Serena, Chile
2
Physics Department, Eastern Mediterranean University, via Mersin 10, 99628, Famagusta, North Cyprus, Turkey
Received:
10
March
2025
Accepted:
16
March
2025
Published online:
8
April
2025
In this study, we explore a static, spherically symmetric black hole solution in the context of a self-interacting Kalb-Ramond field coupled with a global monopole. By incorporating the effects of Lorentz-violating term  and the monopole charge
and the monopole charge 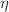 in the KR field, we derive the modified gravitational field equations and analyze the resulting black hole spacetime. The obtained solution exhibits deviations from the Schwarzschild metric with topological defect, as it is influenced by the monopole charge and self-interaction potential. We investigate the thermodynamic properties of the black hole, including its Hawking temperature, entropy, and specific heat, revealing novel stability conditions. Additionally, we perform solar system tests such as perihelion precession, gravitational redshift, light deflection, and time delay of signals to impose constraints on the Lorentz-violating parameter and monopole charge. Our findings suggest that these parameters have to be significantly small, although there are different constraints imposed by individual tests, ranging from
in the KR field, we derive the modified gravitational field equations and analyze the resulting black hole spacetime. The obtained solution exhibits deviations from the Schwarzschild metric with topological defect, as it is influenced by the monopole charge and self-interaction potential. We investigate the thermodynamic properties of the black hole, including its Hawking temperature, entropy, and specific heat, revealing novel stability conditions. Additionally, we perform solar system tests such as perihelion precession, gravitational redshift, light deflection, and time delay of signals to impose constraints on the Lorentz-violating parameter and monopole charge. Our findings suggest that these parameters have to be significantly small, although there are different constraints imposed by individual tests, ranging from 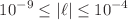 and
and 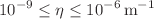 .
.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2025
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




