https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-025-06195-2
Review
Comparison of proton and neutron cascades generated by proton beams in air,  , and
, and  environments
environments
1
Instituto de Física, UFRGS, Av Bento Gonçalves, 9500, 91501-970, Porto Alegre, RS, Brazil
2
Group of Analysis and Simulation of Particles (GASP), IF-UFRGS, Caixa Postal 15051, CEP 91501-970, Porto Alegre, RS, Brazil
Received:
2
December
2024
Accepted:
4
March
2025
Published online:
9
April
2025
In this work, we developed a computational study using Geant4 to investigate potential alterations in particle cascades resulting from multiple interactions between a high-energy particle in air,  , and
, and  environments. Given the extensive range of parameters involved in the research, this study focuses exclusively on the behaviour of protons and neutrons within the cascade for two specific energies of the incident proton, namely 0.5 and 10 GeV. The chosen environment is a cubic box measuring
environments. Given the extensive range of parameters involved in the research, this study focuses exclusively on the behaviour of protons and neutrons within the cascade for two specific energies of the incident proton, namely 0.5 and 10 GeV. The chosen environment is a cubic box measuring 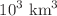 . Our findings reveal distinct differences in the cascade characteristics among the three gases. The distribution of protons and neutrons throughout the environment varies depending on the type of gas and the depth along the axis of incidence. Specifically, for (
. Our findings reveal distinct differences in the cascade characteristics among the three gases. The distribution of protons and neutrons throughout the environment varies depending on the type of gas and the depth along the axis of incidence. Specifically, for ( ), a higher production of protons was observed, whereas for (
), a higher production of protons was observed, whereas for ( ), neutron production was more pronounced under certain conditions. Simulations of the Bragg peak were also conducted, where we observed a shift in the maximum energy loss due to ionisation depending on the environment.
), neutron production was more pronounced under certain conditions. Simulations of the Bragg peak were also conducted, where we observed a shift in the maximum energy loss due to ionisation depending on the environment.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2025
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




