https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-025-06166-7
Regular Article
Elevated temperature effects on the compressive strength and radiation shielding capability of waste granite and marble concrete
1
Civil Engineering Department, Faculty of Engineering, Fayoum University, Fayoum, Egypt
2
Construction and Building Engineering Department, October High Institute for Engineering & Technology, Giza, Egypt
3
Construction and Building Engineering Department, Higher Institute of Engineering, Culture & Science City, Giza, Egypt
4
Geology Department, Faculty of Science, Fayoum University, Fayoum, Egypt
5
Physics Department, Faculty of Science, Fayoum University, Fayoum, Egypt
a im2029@fayoum.edu.eg, islamnabil2228@gmail.com
Received:
24
July
2024
Accepted:
21
February
2025
Published online:
14
April
2025
In an effort to promote the development of sustainable construction practices, this study explores the utilization of construction waste powders as partial cement replacements in concrete. Specifically, granite and marble waste powders were incorporated at varying replacement ratios up to 9% by cement weight. The influence of these waste materials on the compressive strength and radiation shielding effectiveness of ordinary concrete was evaluated under both ambient and elevated temperature conditions (up to 800 °C). The findings revealed significant enhancements in the mechanical properties. Notably, 9% cement replacement ratio with waste granite powder (WGP, 9G) yielded the optimal performance for compressive strength, exhibiting increasements of 25.6% and 33.2% at room temperature and 800 °C, respectively. Similarly, a 5% replacement ratio with waste marble powder (WMP, 5M) demonstrated moderate improvements, achieving gains of 10.3% and 18.7% in compressive strength at room temperature and 800 °C, respectively. The samples at optimal replacement ratios of 9% and 5% for granite and marble, respectively, were tested alongside the control sample (CO) to study their effectiveness in attenuating the various types of radiation. The radiation shielding assessment was evaluated against gamma and neutron using the MC Monte Carlo simulation-5 algorithm and Phy-X software. The gamma ray linear attenuation for concrete mixes (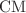 LAC) order for the CO group was found to be CO < 400CO < 600CO < 800CO. The
LAC) order for the CO group was found to be CO < 400CO < 600CO < 800CO. The 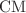 LAC order for the G9 group is G9 < 400G9 < 600G9 < 800G9. The
LAC order for the G9 group is G9 < 400G9 < 600G9 < 800G9. The 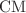 LAC order for the M5 group is M5 < 400M5 < 600M5 < 800M5. The neutron performance (FC) of the CM-concrete samples has values 0.079, 0.075, 0.071, and 0.067 cm−1 for CO, 400CO, 600CO, 800CO samples, 0.094, 0.090, 0.085, and 0.080 cm−1, for G9, 400G9, 600G9, 800G9 samples, and 0.089, 0.083, 0.079, and 0.074 cm−1, for M5, 400M5, 600M5, 800M5 samples, respectively. Thus, the studied CM-concrete samples at room temperature provide the best protection against gamma and fast neutrons. Exposure to high temperatures significantly reduced the gamma and neutron attenuation of concrete samples. However, mixes with optimal granite and marble waste replacements showed enhanced resistance to this effect compared to the control mix.
LAC order for the M5 group is M5 < 400M5 < 600M5 < 800M5. The neutron performance (FC) of the CM-concrete samples has values 0.079, 0.075, 0.071, and 0.067 cm−1 for CO, 400CO, 600CO, 800CO samples, 0.094, 0.090, 0.085, and 0.080 cm−1, for G9, 400G9, 600G9, 800G9 samples, and 0.089, 0.083, 0.079, and 0.074 cm−1, for M5, 400M5, 600M5, 800M5 samples, respectively. Thus, the studied CM-concrete samples at room temperature provide the best protection against gamma and fast neutrons. Exposure to high temperatures significantly reduced the gamma and neutron attenuation of concrete samples. However, mixes with optimal granite and marble waste replacements showed enhanced resistance to this effect compared to the control mix.
© The Author(s) 2025
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.




