https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-025-06037-1
Regular Article
Dynamical 4-D Gauss-Bonnet action from matter-graviton interaction at one-loop
Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, 400076, Mumbai, India
Received:
11
October
2024
Accepted:
17
January
2025
Published online:
3
February
2025
The occurrence of singularities at the centers of black holes suggests that general relativity (GR), although a highly successful model of gravity and cosmology, is inapplicable. This is due to the breakdown of the equivalence principle. Gauss-Bonnet (GB) action is the simplest extension of GR as it possesses second-order equations of motion and is devoid of ghosts. However, in 4-D, the GB action is topological. Recently, Glavan and Lin proposed a mathematical framework that transforms the 4-D GB gravity theory into a non-topological one. However, it has been argued that without a canonical way to choose 4-D from the higher-dimensional space, such a GB gravity is not well-defined in 4-D. Naturally, there has been much interest in having a systematic procedure for making the 4-D GB term non-topological, such as using the counterterm regularization method in 4-D, regularization with the dimensional derivative, and Kaluza-Klein reduction. The current work takes a step in addressing this issue by demonstrating that the rescaling of the GB coupling 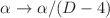 arises from the self-energy correction of gravitons in 4-D using only the established quantum field theoretic techniques. To keep things transparent, we focus on the linearized theory of gravity coupled with matter fields. By computing the one-loop self-energy correction of gravitons induced by the matter fields, we explicitly provide the origin of the prescription provided by Glavan and Lin. We compare the procedure with other regularization procedures like Kaluza-Klein dimensional reduction and conformal scaling regarding the strong coupling problem. Our work naturally opens a new window to considering 4-D Einstein Gauss-Bonnet gravity as the most straightforward modification to GR.
arises from the self-energy correction of gravitons in 4-D using only the established quantum field theoretic techniques. To keep things transparent, we focus on the linearized theory of gravity coupled with matter fields. By computing the one-loop self-energy correction of gravitons induced by the matter fields, we explicitly provide the origin of the prescription provided by Glavan and Lin. We compare the procedure with other regularization procedures like Kaluza-Klein dimensional reduction and conformal scaling regarding the strong coupling problem. Our work naturally opens a new window to considering 4-D Einstein Gauss-Bonnet gravity as the most straightforward modification to GR.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2025
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




