https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-025-06033-5
Regular Article
Modelling the impacts of hospitalization, social dynamics and time delay from an epidemiological approach
Department of Mathematics, Indian Institute of Engineering Science and Technology, 711103, Shibpur, Howrah, India
Received:
16
December
2024
Accepted:
16
January
2025
Published online:
29
January
2025
This research explores the dynamics of an epidemic through the application of an 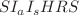 (Susceptible–Asymptomatically infected–Symptomatically infected–Hospitalized–Recovered–Susceptible) epidemiological model, emphasizing the critical role of hospital bed availability and disease transmission by both asymptomatic and symptomatic individuals. The model also incorporates sociological factors such as effective government interventions, social behavioural patterns and public response. A discrete time delay is introduced to the asymptomatically infected compartment to more accurately represent the progression of disease in real-world scenarios. The study examines conditions for existence of both infection-free and endemic steady states based on the concept of basic reproduction number. Sensitivity analysis is conducted to assess how various parameters influence disease transmission. Additionally, the study also investigates changes in system stability through transcritical bifurcation. The analysis of two-parameter bifurcation provides a comprehensive distinction of regions wherein the stability of both the equilibrium points has been thoroughly evaluated. Numerical simulations are provided to illustrate the theoretical findings. The inclusion of time delay in the asymptomatic compartment aims to improve the accuracy of transmission dynamics, facilitating the design of more effective control measures and enhancing epidemic prediction. This extensive research underscores the need for integrating medical resources along with social actions in order to manage and alleviate the effects of epidemics in general.
(Susceptible–Asymptomatically infected–Symptomatically infected–Hospitalized–Recovered–Susceptible) epidemiological model, emphasizing the critical role of hospital bed availability and disease transmission by both asymptomatic and symptomatic individuals. The model also incorporates sociological factors such as effective government interventions, social behavioural patterns and public response. A discrete time delay is introduced to the asymptomatically infected compartment to more accurately represent the progression of disease in real-world scenarios. The study examines conditions for existence of both infection-free and endemic steady states based on the concept of basic reproduction number. Sensitivity analysis is conducted to assess how various parameters influence disease transmission. Additionally, the study also investigates changes in system stability through transcritical bifurcation. The analysis of two-parameter bifurcation provides a comprehensive distinction of regions wherein the stability of both the equilibrium points has been thoroughly evaluated. Numerical simulations are provided to illustrate the theoretical findings. The inclusion of time delay in the asymptomatic compartment aims to improve the accuracy of transmission dynamics, facilitating the design of more effective control measures and enhancing epidemic prediction. This extensive research underscores the need for integrating medical resources along with social actions in order to manage and alleviate the effects of epidemics in general.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2025
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




