https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-025-05982-1
Regular Article
The impact of effective mass mismatch and quantum dot size on the interband absorption and sub-bandgap photocurrent of box-shaped InAs/GaAs quantum dot-intermediate band solar cells
1
Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Erzurum Technical University, Farabi Blv., 25100, Yakutiye, Erzurum, Turkey
2
Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Gazi University, Yukselis Sk., 06570, Cankaya, Ankara, Turkey
a
volkan.kiziloglu@erzurum.edu.tr
Received:
19
August
2024
Accepted:
3
January
2025
Published online:
21
January
2025
The InAs/GaAs quantum dot intermediate band solar cells (QD-IBSCs) have the potential for high conversion efficiency. In practice, their efficiencies have not reached 20%. In this study, the confined energy levels, interband absorption coefficients, and absorbed sub-bandgap photocurrent densities are calculated with QD size using equal effective mass and effective mass mismatch for the box-shaped InAs/GaAs QD system. The four-band k p model was applied to the InAs/GaAs QD system. The energy of IB levels with the effective mass mismatch decreased compared with the equal effective mass. The interband photocurrent density increased with effective mass mismatch since more confined energy states contributed to interband absorption. If the in-plane QD density raised from
p model was applied to the InAs/GaAs QD system. The energy of IB levels with the effective mass mismatch decreased compared with the equal effective mass. The interband photocurrent density increased with effective mass mismatch since more confined energy states contributed to interband absorption. If the in-plane QD density raised from 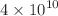
 to
to 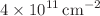 , the interband photocurrent density increased from 0.58 to 5.19
, the interband photocurrent density increased from 0.58 to 5.19 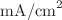 for equal effective mass and 0.99 to 8.38
for equal effective mass and 0.99 to 8.38 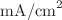 for the effective mass mismatch with 16 nm
for the effective mass mismatch with 16 nm  16 nm
16 nm  6 nm of QD size, under one sun concentration. Increasing the QD size also allows additional IB states within the forbidden band; thus, the interband photocurrent increases with QD size. The interband photocurrent density for 10 nm and 16 nm QD widths is 0.39
6 nm of QD size, under one sun concentration. Increasing the QD size also allows additional IB states within the forbidden band; thus, the interband photocurrent increases with QD size. The interband photocurrent density for 10 nm and 16 nm QD widths is 0.39 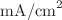 and 0.99
and 0.99 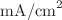 , respectively.
, respectively.
© The Author(s) 2025
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.




