https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-024-05863-z
Regular Article
Particle motion and lensing with plasma of black hole in coincident  gravity coupled to nonlinear electrodynamics
gravity coupled to nonlinear electrodynamics
Department of Mathematics, Shanghai University and Newtouch Center for Mathematics of Shanghai University, 200444, Shanghai, People’s Republic of China
Received:
4
October
2024
Accepted:
12
November
2024
Published online:
2
January
2025
This research is motivated by a study that investigates the features of black hole (BH) under coincident 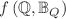 gravity coupled with nonlinear electrodynamics. The study also explores BH shadows and weak gravitational plasma lensing. We examine the effective potential, or ISCO, for the motion of large particles and photons to analyze particle dynamics. To examine the gravitational lensed photons, we suppose the weak gravitational field. Here we consider three plasma domains to fulfill this lensing objective: a non-singular isothermal sphere, a singular isothermal sphere, and uniform plasma. Furthermore, we examine the Gibbons-Werner methodology for calculating the deflection angle of light caused by the BH in a scenario with the weak gravitational field. This illustrates that bending light is a topological and global phenomenon. To accomplish this, we employ the Gauss–Bonnet theorem (GBT) and deduce the Gaussian curvature. Moreover, we calculate the deflection angle at which a plasma medium deflects light. The graphical behavior of BH in vacuum and plasma mediums is also investigated.
gravity coupled with nonlinear electrodynamics. The study also explores BH shadows and weak gravitational plasma lensing. We examine the effective potential, or ISCO, for the motion of large particles and photons to analyze particle dynamics. To examine the gravitational lensed photons, we suppose the weak gravitational field. Here we consider three plasma domains to fulfill this lensing objective: a non-singular isothermal sphere, a singular isothermal sphere, and uniform plasma. Furthermore, we examine the Gibbons-Werner methodology for calculating the deflection angle of light caused by the BH in a scenario with the weak gravitational field. This illustrates that bending light is a topological and global phenomenon. To accomplish this, we employ the Gauss–Bonnet theorem (GBT) and deduce the Gaussian curvature. Moreover, we calculate the deflection angle at which a plasma medium deflects light. The graphical behavior of BH in vacuum and plasma mediums is also investigated.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2025
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.