https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-024-05764-1
Regular Article
Stability and Hopf bifurcation of a HBV infection model with capsids and CTL immune response delay
1
School of Mathematics and Physics, HNP-LAMA, Hunan University of Arts and Science, 415000, Changde, Hunan, People’s Republic of China
2
School of Mathematics and Statistics, HNP-LAMA, Central South University, 410083, Changsha, Hunan, People’s Republic of China
Received:
21
July
2024
Accepted:
19
October
2024
Published online:
4
November
2024
In this paper, an in-host HBV model with two infection routes including cell-virus infection and cell-cell infection, intracellular delay 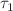 , virus replication delay
, virus replication delay 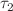 and CTL immune response delay
and CTL immune response delay 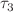 are investigated. Firstly, the positivity and boundedness of all solutions for the model with nonnegative initial values have been established. Next, two key parameters with significant biological importance, the virus reproductive number
are investigated. Firstly, the positivity and boundedness of all solutions for the model with nonnegative initial values have been established. Next, two key parameters with significant biological importance, the virus reproductive number 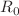 and the CTL immune reproductive number
and the CTL immune reproductive number 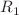 , are derived. Subsequently, the stability of equilibria is analyzed by constructing appropriate Lyapunov functionals and applying LaSalle’s invariance principle. The results indicate that intracellular delay
, are derived. Subsequently, the stability of equilibria is analyzed by constructing appropriate Lyapunov functionals and applying LaSalle’s invariance principle. The results indicate that intracellular delay 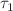 and virus replication delay
and virus replication delay 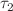 do not affect the stability of the three equilibria. However, a positive CTL immune response delay
do not affect the stability of the three equilibria. However, a positive CTL immune response delay 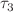 can lead to stability switches at the endemic equilibrium. By treating the CTL immune response delay as a bifurcation parameter, certain conditions for these stability switches are determined. It is concluded that as the CTL immune response delay increases, the endemic equilibrium becomes unstable, resulting in a Hopf bifurcation in the system. Finally, numerical simulations further validate the theoretical findings.
can lead to stability switches at the endemic equilibrium. By treating the CTL immune response delay as a bifurcation parameter, certain conditions for these stability switches are determined. It is concluded that as the CTL immune response delay increases, the endemic equilibrium becomes unstable, resulting in a Hopf bifurcation in the system. Finally, numerical simulations further validate the theoretical findings.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




