https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-024-05716-9
Regular Article
Relativistic calculations of photoionization cross-section of Mg-like Ca IX
1
School of Physical Sciences, Jawaharlal Nehru University, 110067, New Delhi, India
2
Hindu College, University of Delhi, 110078, Delhi, India
3
Department of Physics & Astrophysics, University of Delhi, 110007, Delhi, India
4
Ramjas College, University of Delhi, 110007, Delhi, India
Received:
29
August
2024
Accepted:
23
September
2024
Published online:
24
October
2024
Relativistic calculations of the photoionization cross-sections are carried out for the ground state 1s22p63s2 (1S0) and first three excited states 1s22p63s3p (3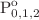 ) of Mg-like Ca IX ion using the Breit–Pauli R-matrix (BPRM) approach. Configuration interaction method (CIV3) is used to construct the target wavefunctions. A total of lowest lying 21 fine structure levels corresponding to 2p6nl (3 ≤ n ≤ 5) configurations are considered for the expansion of target wavefunctions. Reported target state eigen energies of the 21 fine structure levels of core ion Ca X agree with the available data. To assess the accuracy of our BPRM results, we have also performed similar calculations using the fully relativistic Dirac atomic R-matrix code (DARC) for the ground state of Mg-like Ca IX ion. Further, relativistic distorted wave (DW) method is also used for the comparison purpose, and a good agreement has been found with the R-matrix results. The quantum number (n), resonance width (Γ) and resonance energies (Er) of the 3dnp (3P1, 1P1, 3D1, 1D2), 3dnf (3P1, 1P1) and 4snp (3P2, 3P0, 3P1, 1P1) series have also been predicted using Quigley and Berrington (QB) method. We believe that the present results will be helpful for modeling and diagnostics of laboratory and astrophysical plasmas.
) of Mg-like Ca IX ion using the Breit–Pauli R-matrix (BPRM) approach. Configuration interaction method (CIV3) is used to construct the target wavefunctions. A total of lowest lying 21 fine structure levels corresponding to 2p6nl (3 ≤ n ≤ 5) configurations are considered for the expansion of target wavefunctions. Reported target state eigen energies of the 21 fine structure levels of core ion Ca X agree with the available data. To assess the accuracy of our BPRM results, we have also performed similar calculations using the fully relativistic Dirac atomic R-matrix code (DARC) for the ground state of Mg-like Ca IX ion. Further, relativistic distorted wave (DW) method is also used for the comparison purpose, and a good agreement has been found with the R-matrix results. The quantum number (n), resonance width (Γ) and resonance energies (Er) of the 3dnp (3P1, 1P1, 3D1, 1D2), 3dnf (3P1, 1P1) and 4snp (3P2, 3P0, 3P1, 1P1) series have also been predicted using Quigley and Berrington (QB) method. We believe that the present results will be helpful for modeling and diagnostics of laboratory and astrophysical plasmas.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




