https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-024-05701-2
Regular Article
Excitation cross-sections for atomic hydrogen by hydrogen-like ions of helium and carbon
Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, Zarqa University, 13110, Zarqa, Jordan
Received:
24
August
2024
Accepted:
30
September
2024
Published online:
17
October
2024
We present excitation cross-sections of hydrogen (H) atoms by hydrogen-like ions (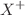 ), employing a four-body classical and quasiclassical trajectory Monte Carlo model (CTMC and QCTMC models). Our calculations encompass impact energies ranging from 1.0 to 100 keV, which hold significant importance in fusion research and plasma physics. We present the total excitation cross-sections, alongside partial excitation cross-sections for the 2s, 2p, 3s, and 3p states of the target atom. A comparison is made between the total and partial excitation cross-sections with previously obtained theoretical and experimental results. Our recent total cross-sections for
), employing a four-body classical and quasiclassical trajectory Monte Carlo model (CTMC and QCTMC models). Our calculations encompass impact energies ranging from 1.0 to 100 keV, which hold significant importance in fusion research and plasma physics. We present the total excitation cross-sections, alongside partial excitation cross-sections for the 2s, 2p, 3s, and 3p states of the target atom. A comparison is made between the total and partial excitation cross-sections with previously obtained theoretical and experimental results. Our recent total cross-sections for 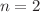 excitation in
excitation in 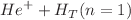 collision shows a good agreement with the Vainshtein-Presnyakov-Sobel'man approximation (VPSA) data, while also presenting lower results compared to the previous Born approximation results and experimental data. Moreover, the CTMC results for partial excited state transitions from 1 to 2s in
collision shows a good agreement with the Vainshtein-Presnyakov-Sobel'man approximation (VPSA) data, while also presenting lower results compared to the previous Born approximation results and experimental data. Moreover, the CTMC results for partial excited state transitions from 1 to 2s in 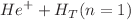 collisions agree well with previously obtained experimental data. On the other hand, the QCTMC results for partial excited state transitions from 1s to 2p in
collisions agree well with previously obtained experimental data. On the other hand, the QCTMC results for partial excited state transitions from 1s to 2p in 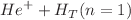 collisions agree well with previous theoretical calculations, especially for energy above 10 keV. Furthermore, the QCTMC cross-section results are higher than the standard CTMC data, demonstrating the significance of the Heisenberg correction term, particularly in the low-energy regime.
collisions agree well with previous theoretical calculations, especially for energy above 10 keV. Furthermore, the QCTMC cross-section results are higher than the standard CTMC data, demonstrating the significance of the Heisenberg correction term, particularly in the low-energy regime.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




