https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-024-05571-8
Regular Article
Study of nuclear corrections on the charged hadron fragmentation functions in a Neural Network global QCD analysis
1
School of Particles and Accelerators, Institute for Research in Fundamental Sciences (IPM), P.O.Box 19395-5531, Tehran, Iran
2
Faculty of Physics and Applied Computer Science, AGH University, Al. Mickiewicza 30, 30-055, Kraków, Poland
3
Department of Physics, University of Science and Technology of Mazandaran, P.O.Box 48518-78195, Behshahr, Iran
Received:
26
November
2023
Accepted:
19
August
2024
Published online:
6
September
2024
In this work, we present a new global QCD analyses, referred to as PKHFF.23, for charged pion, kaon, and unidentified light hadrons. We utilize a Neural Network to fit the high-energy lepton-lepton and lepton-hadron scattering data, enabling us to determine parton-to-hadron fragmentation functions (FFs) at next-to-leading-order (NLO) accuracy. The analyses include all available single-inclusive 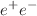 annihilation (SIA) and semi-inclusive deep-inelastic scattering (SIDIS) data from the COMPASS Collaboration for charged pions, kaons, and unidentified light hadrons. Taking into account the most recent nuclear parton distribution functions (nuclear PDFs) available in the literature, we evaluate the effect of nuclear corrections on the determination of light hadrons FFs. The Neural Network parametrization, enriched with the Monte Carlo methodology for uncertainty estimations, is employed for all sources of experimental uncertainties and the proton PDFs. Our results indicate that incorporating nuclear corrections has a marginal impact on the central values of FFs and their corresponding uncertainty bands. The inclusion of such corrections does not significantly affect the fit quality of the data as well. The study suggests that while nuclear corrections are a consideration, their impact in such QCD analysis is limited.
annihilation (SIA) and semi-inclusive deep-inelastic scattering (SIDIS) data from the COMPASS Collaboration for charged pions, kaons, and unidentified light hadrons. Taking into account the most recent nuclear parton distribution functions (nuclear PDFs) available in the literature, we evaluate the effect of nuclear corrections on the determination of light hadrons FFs. The Neural Network parametrization, enriched with the Monte Carlo methodology for uncertainty estimations, is employed for all sources of experimental uncertainties and the proton PDFs. Our results indicate that incorporating nuclear corrections has a marginal impact on the central values of FFs and their corresponding uncertainty bands. The inclusion of such corrections does not significantly affect the fit quality of the data as well. The study suggests that while nuclear corrections are a consideration, their impact in such QCD analysis is limited.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




