https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-024-05568-3
Regular Article
Fabrication, photovoltaic analysis, and electrical characterization of Au/ZnTPyP/p-Si/Ag heterojunction under gamma radiation effect for solar cell applications
1
Physics Department, Faculty of Science, Port Said University, 42522, Port Said, Egypt
2
Physics and Mathematical Engineering Department, Faculty of Engineering, Port Said University, 42526, Port Said, Egypt
Received:
24
April
2024
Accepted:
19
August
2024
Published online:
9
September
2024
The main objective of the current study is to investigate the impact of gamma rays on the characteristics and behavior of a fabricated heterojunction device based on tetra pyridyl-porphine zinc (ZnTPyP). The importance of this study includes determining critical parameters such as conversion efficiency (η). A cobalt-60 gamma source has been employed to investigate the effects of gamma exposure dosages ranging from 0 to 5 kGy on the morphological and optical features of the studied material. An atomic force microscope (AFM) was used to examine the morphological characteristics of the ZnTPyP film that formed on the glass substrate. The thin film’s optical characteristics were investigated on quartz for both as-deposited and irradiated films at various gamma doses (1 kGy and 3 kGy). Additionally, ZnTPyP is evaporated on p-type silicon substrates to create ZnTPyP/p-Si heterojunction. The current–voltage (I–V) curves at various doses of gamma radiation at 0, 1, 3, and 5 kGy for Au/ ZnTPyP /p-Si/Ag heterojunction device are experimentally measured. The predominant conduction processes are the thermionic emission and single-trap space-charge-limited current (SCLC). Furthermore, the values of the barrier height 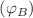 are estimated using two different methods, including I–V method and Norde’s equations at different doses, and their values are comparable. Under illumination at 0 kGy, we found the values of short-circuit current (Isc), open-circuit voltage (Voc), and photoconversion efficiency (η) to be 0.92 mA, 0.41 V, and 4.28%, respectively. On the hand, some important optical parameters are determined for both as-deposited and irradiated ZnTPyP films, such as skin depth (δ), and found that δ values reduce with increasing gamma doses, reflecting the efficiency and performance of photovoltaic cells. Finally, the study indicated the alteration in the studied optical parameters and slightly enhanced the Au/ZnTPyP/p-Si/Ag heterojunction efficiency when subjected to gamma radiation.
are estimated using two different methods, including I–V method and Norde’s equations at different doses, and their values are comparable. Under illumination at 0 kGy, we found the values of short-circuit current (Isc), open-circuit voltage (Voc), and photoconversion efficiency (η) to be 0.92 mA, 0.41 V, and 4.28%, respectively. On the hand, some important optical parameters are determined for both as-deposited and irradiated ZnTPyP films, such as skin depth (δ), and found that δ values reduce with increasing gamma doses, reflecting the efficiency and performance of photovoltaic cells. Finally, the study indicated the alteration in the studied optical parameters and slightly enhanced the Au/ZnTPyP/p-Si/Ag heterojunction efficiency when subjected to gamma radiation.
© The Author(s) 2024
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.




