https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-024-05565-6
Regular Article
Hindrance of complete fusion in  O +
O +  Ho reaction at above the barrier energies: Role of angular momentum
Ho reaction at above the barrier energies: Role of angular momentum
1
Department of Physics, Aligarh Muslim University, 202 002, Aligarh, U.P, India
2
MANUU Polytechnic Darbhanga, Maulana Azad National Urdu University, 500 032, Hyderabad, Telangana, India
3
Department of Physics, Hindu College, 244 001, Moradabad, U.P, India
4
Department of Physics, Bareilly College, 243 005, Bareilly, U.P, India
5
Amity Institute of Nuclear Science and Technology, Amity University, 110 025, Noida, U.P, India
Received:
2
July
2024
Accepted:
16
August
2024
Published online:
17
September
2024
In an experimental approach to investigate the role of projectile structure in above barrier fusion suppression, complete and incomplete fusions are studied using the  O +
O +  Ho system at
Ho system at 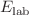
 78–104 MeV. Off-line
78–104 MeV. Off-line 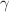 -ray measurement technique is utilized for the measurement of excitation function of the populated evaporation residues. Complete and incomplete fusion reaction channels have been identified in the light of statistical model code PACE4. Extending the approach of Mukeru et al. (Nucl Phys A 996:121700, 2020) to fusion reaction induced by tightly bound projectile
-ray measurement technique is utilized for the measurement of excitation function of the populated evaporation residues. Complete and incomplete fusion reaction channels have been identified in the light of statistical model code PACE4. Extending the approach of Mukeru et al. (Nucl Phys A 996:121700, 2020) to fusion reaction induced by tightly bound projectile  O over different targets, cutoff angular momentum is extracted from experimentally measured complete fusion cross section data at different beam energies. Degree of fusion suppression is estimated by exposing the extracted fusion function to universal fusion function. Sum-rule model-based critical angular momentum and incomplete fusion fraction are found to be strongly driven by Coulomb repulsion and reduced mass of the projectile–target system.
O over different targets, cutoff angular momentum is extracted from experimentally measured complete fusion cross section data at different beam energies. Degree of fusion suppression is estimated by exposing the extracted fusion function to universal fusion function. Sum-rule model-based critical angular momentum and incomplete fusion fraction are found to be strongly driven by Coulomb repulsion and reduced mass of the projectile–target system.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




