https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-024-05398-3
Regular Article
Exploring the magnetic and non-magnetic characteristics of 2D hexagonal and tetragonal CrP structures
1
Department of Physics, Yasouj University, 75914-353, Yasouj, Iran
2
Department of Mathematics, Yasouj University, 75914-353, Yasouj, Iran
Received:
13
April
2024
Accepted:
24
June
2024
Published online:
9
July
2024
The magnetic properties of monolayers of hexagonal and tetragonal CrP have been studied using density functional calculations. Cohesive energy, phonon spectra, and Crystal Orbital Hamilton Population analysis were performed on both the magnetic and non-magnetic phases of h-CrP and t-CrP to determine the more stable phases. The results indicate that the ferromagnetic phase is unstable in h-CrP, but stable in t-CrP. The impact of strain on the electronic structure and magnetic properties of t-CrP was also studied. The findings suggest that this single-layer compound is a semi-metal with an indirect energy gap in the spin-down channel. Tensile strain slightly enhances the magnetic moment of the Cr atoms, while compressive strain reduces it. The compounds exhibit a consistent behavior with a total magnetic moment of 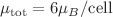 across the range of applied strain.
across the range of applied strain.
Reza Khordad, Behrooz Vaseghi, Jaafar Jalilian and Heydar Ali Mardani-Fard have contributed equally to this work.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




