https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-024-05376-9
Regular Article
Exploring the physical attributes of NaCaX (X = As, Sb) semiconductors by first principles calculations
1
Department of Physics, Bahawalnagar Campus, The Islamia University of Bahawalpur, Punjab, Pakistan
2
Department of Physics, Government Sadiq College Women University Bahawalpur, Punjab, Pakistan
3
Department of Mathematics and Science, College of Humanities and Sciences, Prince Sultan University, Riyadh, 11586, Saudi Arabia
a
alirazashahab8@gmail.com
g
nasir.rasool@iub.edu.pk
Received:
9
April
2024
Accepted:
17
June
2024
Published online:
1
July
2024
Half-Heusler compounds have attracted much interest as adaptable materials for various real-world uses, such as photoconductive devices, thermoelectric, spintronics and catalysis. This work aimed to examine structural, phononic, optoelectronic and physicomechanical characteristics of two distinct half-Heusler NaCaX (X = As, Sb) compounds. The density functional theory-based VASP and WIEN2k codes have been employed. For computing electronic properties, three exchange–correlation functionals have been considered in the computations including LDA, PBEsol & mBJ. The results revealed that the F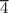 3m phase is structurally stable, with lattice constants of 6.9591 Å for NaCaAs and 7.3969 Å for NaCaSb in agreement with experimental findings. The structural, mechanical and dynamic stability of compounds was also confirmed. Analysis of the partial charge distribution in the highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) and lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) indicated that the “As-atom” predominantly bore the charge density, suggesting a p-type interaction for NaCaAs. For NaCaSb, both the “Sb-atom” (majorly) and “Ca-atom” (minorly) played a similar role, implying the s-type and p-type interaction. Furthermore, the authors investigated various optoelectronic properties viz. band structure, the density of states, complex dielectric function, optical conductivity, energy loss function, reflectivity, extinction coefficient, net effective electrons (Neff.), refractive index and have discussed in detail. Furthermore, a detailed explanation of the physical and mechanical properties, the mechanical directional dependence, charge transfer and bonding process have been provided.
3m phase is structurally stable, with lattice constants of 6.9591 Å for NaCaAs and 7.3969 Å for NaCaSb in agreement with experimental findings. The structural, mechanical and dynamic stability of compounds was also confirmed. Analysis of the partial charge distribution in the highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) and lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) indicated that the “As-atom” predominantly bore the charge density, suggesting a p-type interaction for NaCaAs. For NaCaSb, both the “Sb-atom” (majorly) and “Ca-atom” (minorly) played a similar role, implying the s-type and p-type interaction. Furthermore, the authors investigated various optoelectronic properties viz. band structure, the density of states, complex dielectric function, optical conductivity, energy loss function, reflectivity, extinction coefficient, net effective electrons (Neff.), refractive index and have discussed in detail. Furthermore, a detailed explanation of the physical and mechanical properties, the mechanical directional dependence, charge transfer and bonding process have been provided.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.





