https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-024-05339-0
Regular Article
Analysis of a delayed MISCR rumor spread model with refutation mechanism
1
Department of Mathematics, Indian Institute of Engineering Science and Technology, Shibpur, 711 103, Howrah, India
2
Department of Mathematics, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, India
Received:
26
February
2024
Accepted:
30
May
2024
Published online:
28
June
2024
The sustainability of the social order is chasing the severe challenge of increasing the spread of rumors on social media. The popularity of social media platforms is disastrously contributing to the spread of harmful rumors, posing a threat to society. In this article, we have formulated MISCR model by incorporating mainstream media to a social media population containing ignorant, spreader, counter-rumor spreader and stifler. In addition, a time delay is introduced in the transformation process of ignorant individuals after interaction with counter-rumor spreaders. First, the qualitative behaviors of the corresponding non-delayed system are studied, followed by the derivation of the spreading threshold of rumor 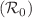 . Subsequently, sensitivity of
. Subsequently, sensitivity of 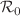 with respect to input parameters is studied using normalized forward sensitivity analysis. To illustrate the impact of delay on rumor propagation existence conditions of Hopf and Hopf–Hopf bifurcations have been analyzed. Also, sufficient conditions for Hopf bifurcation regarding the interference of counter-rumor spreaders are determined. Subsequently, some numerical simulations are demonstrated to validate the analytical results. Moreover, some complex phenomena like stability switch, chaos are observed numerically. It is also found that the governmental input in refutation mechanism can effectively remove the chaos.
with respect to input parameters is studied using normalized forward sensitivity analysis. To illustrate the impact of delay on rumor propagation existence conditions of Hopf and Hopf–Hopf bifurcations have been analyzed. Also, sufficient conditions for Hopf bifurcation regarding the interference of counter-rumor spreaders are determined. Subsequently, some numerical simulations are demonstrated to validate the analytical results. Moreover, some complex phenomena like stability switch, chaos are observed numerically. It is also found that the governmental input in refutation mechanism can effectively remove the chaos.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




