https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-024-05302-z
Regular Article
Collision of perturbed soliton in discrete ferromagnetic spin chain with nearest neighbor and next nearest neighbor Dzyaloshinskii–Moriya interaction
Department of Physics, School of Advanced Sciences, Vellore Institute of Technology, Chennai Campus, Kelambakkam Road, 600 127, Chennai, Tamilnadu, India
Received:
18
July
2023
Accepted:
21
May
2024
Published online:
6
June
2024
We study the effect of next nearest neighbor Dzyaloshinskii–Moriya (DM) interaction on collision of perturbed solitons in a discrete ferromagnetic spin chain. This system includes nearest neighbor and next nearest neighbor DM interaction. We consider the Heisenberg Hamiltonian model of ferromagnetic spin chain, which takes into account both nearest neighbor and next nearest neighbor DM interaction. Using the quasi-classical approximation, we transform the Hamiltonian into the discrete nonlinear Schr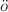 dinger (DNLS) equation. The DNLS equation describes the complete dynamics of the ferromagnetic spin chain. The discrete Hirota bilinearization method is employed to construct the one-soliton and two-soliton solutions of the DNLS equation. The two-soliton solutions are utilized to discuss the impact of nearest neighbor and next nearest neighbor DM interactions on the collision of solitons in the ferromagnetic spin chain. Additionally, we delve into the phase shift and intensity redistribution during the collision of solitons in a ferromagnetic spin chain.
dinger (DNLS) equation. The DNLS equation describes the complete dynamics of the ferromagnetic spin chain. The discrete Hirota bilinearization method is employed to construct the one-soliton and two-soliton solutions of the DNLS equation. The two-soliton solutions are utilized to discuss the impact of nearest neighbor and next nearest neighbor DM interactions on the collision of solitons in the ferromagnetic spin chain. Additionally, we delve into the phase shift and intensity redistribution during the collision of solitons in a ferromagnetic spin chain.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




