https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-024-05290-0
Regular Article
Nuclear modification factor in Pb-Pb and p-Pb collisions at 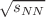 = 5.02 TeV at LHC energies using Boltzmann transport equation with tsallis blast wave description
= 5.02 TeV at LHC energies using Boltzmann transport equation with tsallis blast wave description
1
Department of Physics, University of Allahabad, Prayagraj, 211002, UP, India
2
Variable Energy Cyclotron Centre, 1/AF- Bidhannagar, 700064, Kolkata, India
Received:
5
October
2023
Accepted:
18
May
2024
Published online:
6
June
2024
In this article, we have studied the nuclear modification factor measured in the most central and peripheral Pb-Pb (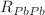 ) and p-Pb collisions (
) and p-Pb collisions (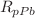 ) for
) for 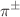 ,
, 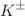 ,
, 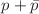 , (
, (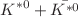 )/2,
)/2, 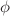 and
and 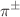 ,
, 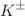 ,
, 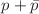 , respectively at Large hadron collider (LHC) energy of
, respectively at Large hadron collider (LHC) energy of 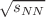 = 5.02 TeV. We have also analysed the experimental data of transverse momentum (
= 5.02 TeV. We have also analysed the experimental data of transverse momentum (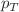 ) spectra for these identified hadrons at LHC for Pb-Pb as well as for p-Pb collisions. We have used Boltzmann transport equation (BTE) in relaxation time approximation (RTA) for this analysis. The Tsallis statistics is used as an initial distribution function and the Tsallis blast wave (TBW) model is employed as an equilibrium distribution in BTE. The present model fits the measured transverse momentum spectra,
) spectra for these identified hadrons at LHC for Pb-Pb as well as for p-Pb collisions. We have used Boltzmann transport equation (BTE) in relaxation time approximation (RTA) for this analysis. The Tsallis statistics is used as an initial distribution function and the Tsallis blast wave (TBW) model is employed as an equilibrium distribution in BTE. The present model fits the measured transverse momentum spectra, 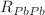 , and
, and 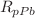 successfully upto
successfully upto 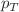 = 8 GeV/c with a reasonable
= 8 GeV/c with a reasonable 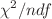 for all the considered hadrons at various centralities. The experimental data for
for all the considered hadrons at various centralities. The experimental data for 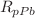 are generated using the particle yields at p-Pb and pp collisions where number of binary collisions are taken from Glauber model calculations. We find that the average transverse flow velocity (
are generated using the particle yields at p-Pb and pp collisions where number of binary collisions are taken from Glauber model calculations. We find that the average transverse flow velocity (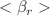 ) decreases with the mass as well as when one move from the central collisions to the peripheral collisions. These findings are inline with the results of the hydrodynamics-inspired model calculations.
) decreases with the mass as well as when one move from the central collisions to the peripheral collisions. These findings are inline with the results of the hydrodynamics-inspired model calculations.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




