https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-024-05113-2
Regular Article
Heat transfer enhancement analysis of mixed convection 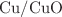 –water magneto-hybrid nanofluid flow in a square enclosure with hot and cold slits in non-Darcy porous medium
–water magneto-hybrid nanofluid flow in a square enclosure with hot and cold slits in non-Darcy porous medium
Department of Mathematics, School of Advances Sciences, Vellore Institute of Technology, 632014, Vellore, India
Received:
3
February
2024
Accepted:
20
March
2024
Published online:
5
April
2024
The fluid flow over an extending cavity has many applications in different fields which include manufacturing processes, treatment of various diseases, destruction of cancer tissue, artificial lungs and radiators, heat and mass transfer, biomedical applications, environmental science, and energy production. The heat transfer investigated mixed convection MHD with 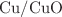 –water hybrid nanofluid flow in a square cavity with a non-Darcy porous medium. In this study, the MAC (Marker and Cell) technique is to solve the resulting governing non-dimensional partial differential equation within a staggered grid system. The
–water hybrid nanofluid flow in a square cavity with a non-Darcy porous medium. In this study, the MAC (Marker and Cell) technique is to solve the resulting governing non-dimensional partial differential equation within a staggered grid system. The  software is used to obtain the contours of streamlines and isotherms. In comparison with prior research, the average Nusselt number obtained under identical conditions validates the accuracy of the current study’s findings. The impact of magnetic field
software is used to obtain the contours of streamlines and isotherms. In comparison with prior research, the average Nusselt number obtained under identical conditions validates the accuracy of the current study’s findings. The impact of magnetic field  , non-Darcy
, non-Darcy  , and heat sink/source
, and heat sink/source  parameters are discussed. The results of the current study assert that the square cavity of heat and energy transfer increases as the non-Darcy parameter value
parameters are discussed. The results of the current study assert that the square cavity of heat and energy transfer increases as the non-Darcy parameter value 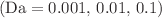 increases. The heat transfer rate is very slow as the Hartmann number
increases. The heat transfer rate is very slow as the Hartmann number 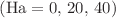 increases. Finally, heat transfer increases as the influence of the heat generation/absorption parameter
increases. Finally, heat transfer increases as the influence of the heat generation/absorption parameter 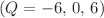 also increases.
also increases.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




