https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-024-05031-3
Regular Article
Exciton magnetic polaron in Cd1–xMnxTe single semimagnetic quantum ring
Department of Electrical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology, Powai, 400076, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India
a
pkalpana.physics@gmail.com
b
bm@ee.iitb.ac.in
Received:
18
September
2023
Accepted:
21
February
2024
Published online:
8
April
2024
Magnetically doped nanostructures can significantly enhance the interaction between the band carriers and the dopant atoms. Motivated by the demonstration of the enhanced sp-d exchange interaction in quantum confined structures with the increased stability of the exciton magnetic polaron, we report the quantitative and qualitative analyses of the exciton magnetic polaron formation in CdTe/Cd1–xMnxTe diluted magnetic quantum ring. The quantum ring with two different configurations: (i) the non-magnetic ring (CdTe) embedded in the semimagnetic Cd1–xMnxTe matrix and (ii) magnetically non-uniform quantum structures embedded with 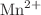 ions both in the ring and in the barrier regimes, has been investigated for various mole fractions of the Mn dopants. The larger polaron binding energy (
ions both in the ring and in the barrier regimes, has been investigated for various mole fractions of the Mn dopants. The larger polaron binding energy (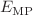 ) of 23 meV is estimated for the 5% molar Mn contents compared to the other quantum confined systems made of CdMnTe. The magnetic field dependence of the MP energy and the corresponding polaron parameters such as exchange field, localization radius of the MP, and the degree of circular polarization induced by the external applied magnetic field at T = 4.2 K have been derived. The obtained results are in excellent agreement with the trend of the significant degradation of
) of 23 meV is estimated for the 5% molar Mn contents compared to the other quantum confined systems made of CdMnTe. The magnetic field dependence of the MP energy and the corresponding polaron parameters such as exchange field, localization radius of the MP, and the degree of circular polarization induced by the external applied magnetic field at T = 4.2 K have been derived. The obtained results are in excellent agreement with the trend of the significant degradation of 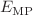 in an external magnetic field and with the contradictory tendencies of
in an external magnetic field and with the contradictory tendencies of 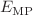 for the QR with configurations (i) and (ii), as reported from the time-integrated measurements based on selective excitation for the quantum systems made of CdMnTe and other DMS materials.
for the QR with configurations (i) and (ii), as reported from the time-integrated measurements based on selective excitation for the quantum systems made of CdMnTe and other DMS materials.
A correction to this article is available online at https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-024-05213-z.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




