https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-024-05085-3
Regular Article
Studying the impact of biaxial strain on the electronic and optical properties of 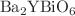 and
and 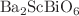 double perovskites for optoelectronic applications: ab initio calculations
double perovskites for optoelectronic applications: ab initio calculations
1
Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Technology, Ropar, 140001, Rupnagar, Punjab, India
2
Department of Physics, IKG Punjab Technical University, 144603, Kapurthala, Punjab, India
Received:
25
November
2023
Accepted:
11
March
2024
Published online:
24
March
2024
We report the electronic, vibrational, and optical properties of specific double perovskites, i.e., 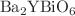 (BYBO) and
(BYBO) and 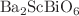 (BSBO) using first-principle calculations based on density functional theory. The stability of both the compounds has been confirmed by their elastic and thermodynamic properties. The effects of strain on the electronic and optical properties of BYBO and BSBO; with an external range of
(BSBO) using first-principle calculations based on density functional theory. The stability of both the compounds has been confirmed by their elastic and thermodynamic properties. The effects of strain on the electronic and optical properties of BYBO and BSBO; with an external range of 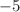 to
to 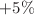 . Electronic properties show semiconducting behavior with bandgap (
. Electronic properties show semiconducting behavior with bandgap (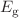 ) values of;
) values of; 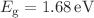 and
and 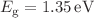 , for BYBO and BSBO, respectively with indirect bandgap alignment. On application on external tensile strain
, for BYBO and BSBO, respectively with indirect bandgap alignment. On application on external tensile strain 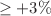 , the bandgap of BYBO and BSBO undergoes a transition from indirect alignment to direct alignment, whereas the electronic bandgap alignment does not change with compressive strain. Interestingly, the magnitude of the bandgap shows contrasting behavior, i.e., the bandgap increases (up to 0.9–1 eV) with compressive strain and decreases (up to 0.7–0.8 eV) with tensile strain. The wavelength values calculated in the absorption spectra of the pristine samples are 373 nm for BYBO and 434 nm for BSBO; suggesting their potential suitability as alternatives for “solar cell” applications, photodetectors, superlenses, photovoltaic devices, etc.
, the bandgap of BYBO and BSBO undergoes a transition from indirect alignment to direct alignment, whereas the electronic bandgap alignment does not change with compressive strain. Interestingly, the magnitude of the bandgap shows contrasting behavior, i.e., the bandgap increases (up to 0.9–1 eV) with compressive strain and decreases (up to 0.7–0.8 eV) with tensile strain. The wavelength values calculated in the absorption spectra of the pristine samples are 373 nm for BYBO and 434 nm for BSBO; suggesting their potential suitability as alternatives for “solar cell” applications, photodetectors, superlenses, photovoltaic devices, etc.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




