https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-024-05043-z
Regular Article
Unveiling the effects of azimuthal angle and superimposed magnetic bias fields on the nonlinear magnetization dynamics of superparamagnetic nanoparticles
1
Academy of Montpellier, 31 rue de l’Université, 67000, Montpellier, France
2
Physics Department, College of Science, King Faisal University, 31982, Al Ahsa, Saudi Arabia
3
Department of Chemistry, University of Alberta, T6G 2G2, Edmonton, AB, Canada
4
Physics Department, Faculty of Science, Assiut University, 71516, Assiut, Egypt
5
Physics Department College of Science, University of Ha’il, Ha’il, Saudi Arabia
a
bachir.ouari@ac-montpellier.fr
b
nrekik@kfu.edu.sa
Received:
21
November
2023
Accepted:
25
February
2024
Published online:
16
March
2024
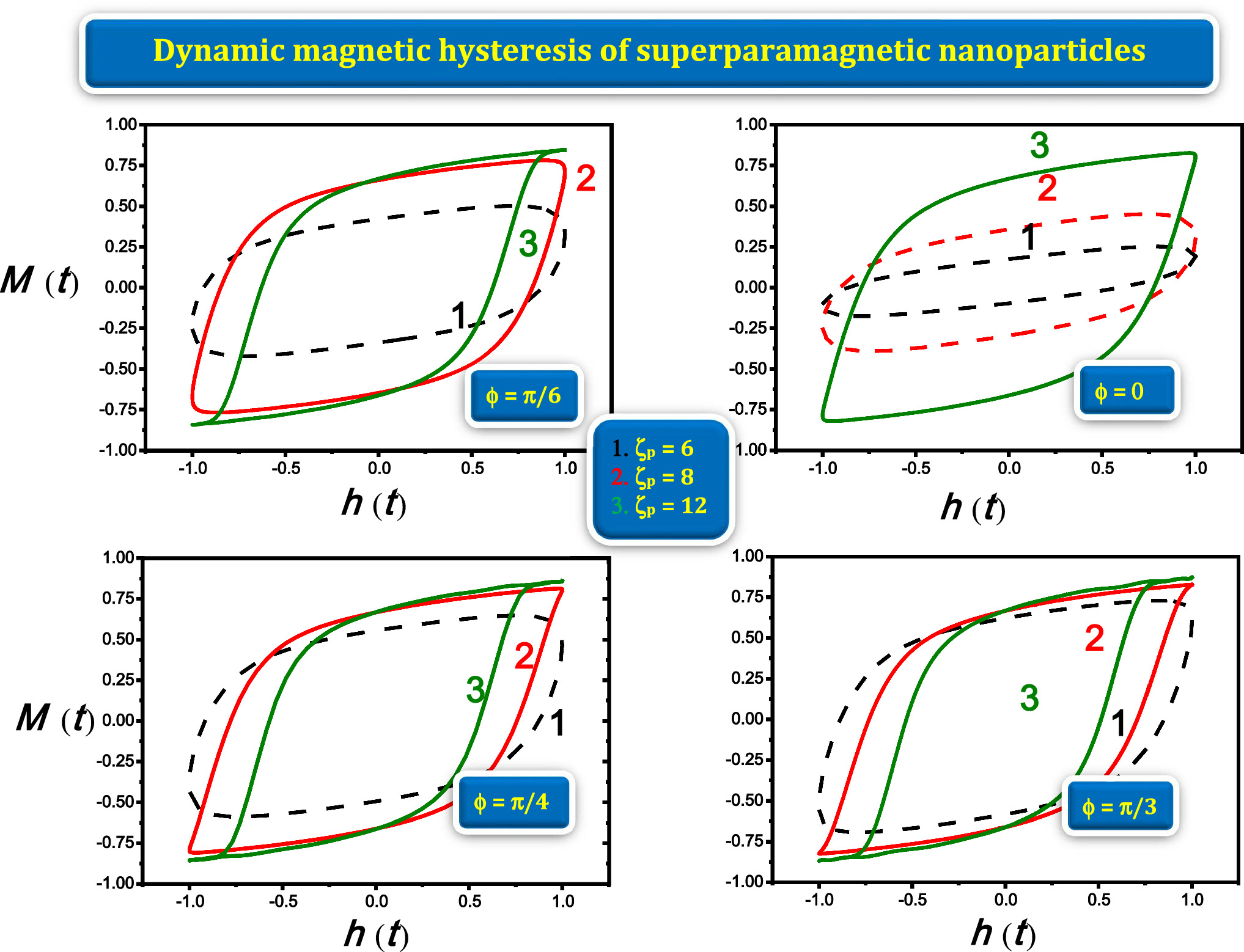
Superparamagnetic nanoparticles provide an efficient way of magnetic recording media based on their magnetization dynamics. This process is predominately governed by the nonlinear magnetic susceptibility. The most accurate approach for performing the calculation of the nonlinear magnetic susceptibility requires the determination of the nonlinear magnetization’ response in thermal agitation subsistence. The recently developed procedure is rationalized by the equation of Langevin that is the equation of Gilbert preserved by an increased random field h (t) as well as processed by Gaussian white noise properties. Moreover, the procedure is predominantly considering the thermal fluctuations of the individual particle magnetization M (t). Nevertheless, this prediction relied on representing the nonlinear magnetic susceptibility and dynamic magnetic hysteresis (DMH) for any direction of AC field strengths. Herein, an illustration of the effect of the azimuthal angle 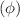 on the DMH and the nonlinear AC susceptibility of nanoparticles is elucidated. A set of linear differential equations describing the statistical moments with infinite hierarchy-recurrence proprieties and susceptible to elucidate the dynamics governing the magnetization of a peculiar single superparamagnetic nanoparticle is established. The method has demonstrated low computational cost and high accuracy by considering the average of the fundamental stochastic Landau–Lifshitz–Gilbert equation in the course of its achievements. It has been found that a strong reliance of the nonlinear AC susceptibility and the DMH on the azimuthal angle
on the DMH and the nonlinear AC susceptibility of nanoparticles is elucidated. A set of linear differential equations describing the statistical moments with infinite hierarchy-recurrence proprieties and susceptible to elucidate the dynamics governing the magnetization of a peculiar single superparamagnetic nanoparticle is established. The method has demonstrated low computational cost and high accuracy by considering the average of the fundamental stochastic Landau–Lifshitz–Gilbert equation in the course of its achievements. It has been found that a strong reliance of the nonlinear AC susceptibility and the DMH on the azimuthal angle 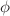 is observed
is observed
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.