https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-024-04987-6
Regular Article
Spatiotemporal patterns in a network of locally and magnetically coupled VDPCL oscillators
1
Research Unit of Condensed Matter, Electronics, and Signal Processing, Department of Physics, University of Dschang, P.O. Box 67, Dschang, Cameroon
2
Research Unit of Industrial Systems Engineering and Environment, Fotso-Victor University Institute of Technology, University of Dschang, P.O. Box 134, Bandjoun, Cameroon
3
Research Unit of Automation and Applied Computer, Fotso-Victor University Institute of Technology, University of Dschang, P.O. Box 134, Bandjoun, Cameroon
Received:
8
November
2023
Accepted:
9
February
2024
Published online:
25
February
2024
Recent advancements in wireless magnetic induction technology have enabled applications in both wireless power and data transfer. This study investigates the spatiotemporal dynamics of a network of 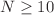 magnetically coupled VDPCL oscillator (Van der Pol oscillator coupled to linear circuit). The focus is on exploring these dynamics based on magnetic coupling coefficients. Using statistical measures namely the strength of incoherence, the cross-correlation coefficient, and a classification algorithm described in the text, synchronized states within the network are categorized. Numerical simulations reveal diverse dynamics, including coherence, incoherence, chimera states, solitary states, and multicluster behaviors, influenced by initial conditions and magnetic coefficients. Also, specific dynamics such as solitary at the cluster state, clustered solitary state and water-like traveling cluster waves are obtained. These phenomena contribute to a richer understanding of the complex dynamics emerging in magnetically coupled oscillator networks. To validate our findings, PSPICE-based circuit simulations are performed for
magnetically coupled VDPCL oscillator (Van der Pol oscillator coupled to linear circuit). The focus is on exploring these dynamics based on magnetic coupling coefficients. Using statistical measures namely the strength of incoherence, the cross-correlation coefficient, and a classification algorithm described in the text, synchronized states within the network are categorized. Numerical simulations reveal diverse dynamics, including coherence, incoherence, chimera states, solitary states, and multicluster behaviors, influenced by initial conditions and magnetic coefficients. Also, specific dynamics such as solitary at the cluster state, clustered solitary state and water-like traveling cluster waves are obtained. These phenomena contribute to a richer understanding of the complex dynamics emerging in magnetically coupled oscillator networks. To validate our findings, PSPICE-based circuit simulations are performed for 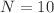 oscillators aligning well with the predictions of mathematical models. This study not only sheds light on the diverse dynamics achievable in magnetically coupled oscillator networks but also holds implications for advancing wireless technologies. The systematic classification and validation through PSPICE simulations contribute to the robustness of our findings and their applicability in practical scenarios.
oscillators aligning well with the predictions of mathematical models. This study not only sheds light on the diverse dynamics achievable in magnetically coupled oscillator networks but also holds implications for advancing wireless technologies. The systematic classification and validation through PSPICE simulations contribute to the robustness of our findings and their applicability in practical scenarios.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




