https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-024-04959-w
Regular Article
Isotropic and anisotropic neutron star structure in 4D Einstein–Gauss–Bonnet Gravity
Physics Department and Biruni Observatory, Shiraz University, 71454, Shiraz, Iran
Received:
21
July
2023
Accepted:
31
January
2024
Published online:
16
February
2024
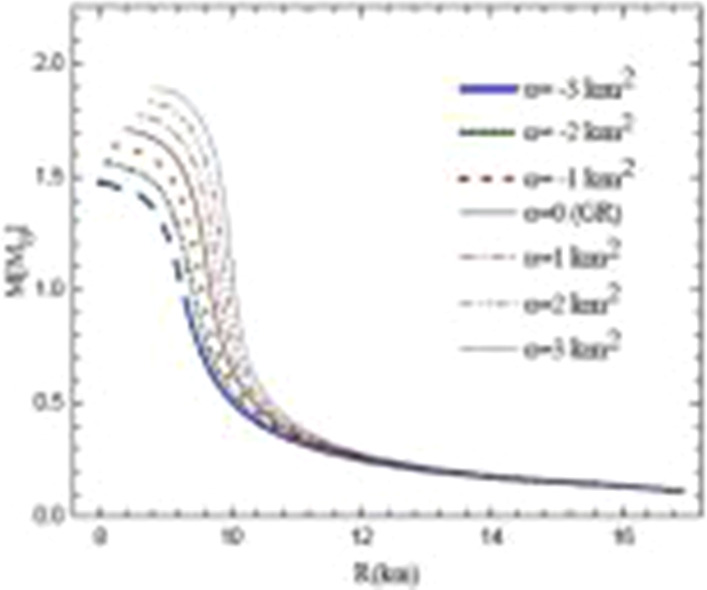
With regard to the coupling constant and the strong magnetic field of neutron stars, we have studied these stars in the 4D Einstein–Gauss–Bonnet (4D EGB) gravity model in order to grasp a better understanding of these objects. In this paper, we have shown that the neutron star properties are considerably affected by the coupling constant and magnetic field. We have found that as a consequence of the strong magnetic field and the coupling constant, the maximum mass and radius of a neutron star are increasing functions of the coupling constant, while Schwarzschild radius, compactness, surface gravitational redshift, and Kretschmann scalar are decreasing functions. Additionally, our study has shown that the physical properties of a magnetized neutron star are greatly influenced not only by the strong magnetic field, but also by the anisotropy. Moreover, we have shown that to obtain the hydrostatic equilibrium configuration of the magnetized material, both the local anisotropy effect and the anisotropy due to the magnetic field should be considered. Finally, we have found that in the anisotropic magnetized neutron stars, the maximum mass and radius do not always increase with increasing the internal magnetic field.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.