https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-024-04940-7
Regular Article
Analysis of thermal characteristics and flow structure in a heat exchanger tube equipped with a lattice elliptical turbulator utilizing rGo/Co3O4 hybrid nanofluid
1
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Jundi-Shapur University of Technology, Dezful, Iran
2
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Alzahra University, 09121328094, Tehran, Iran
3
Optimization of Energy and Carbon Consumption, National Iranian Gas Company, Semnan, Iran
a
Mr.Assari@alzahra.ac.ir
b
hadi_banihashemi@yahoo.com
Received:
30
May
2023
Accepted:
25
January
2024
Published online:
8
February
2024
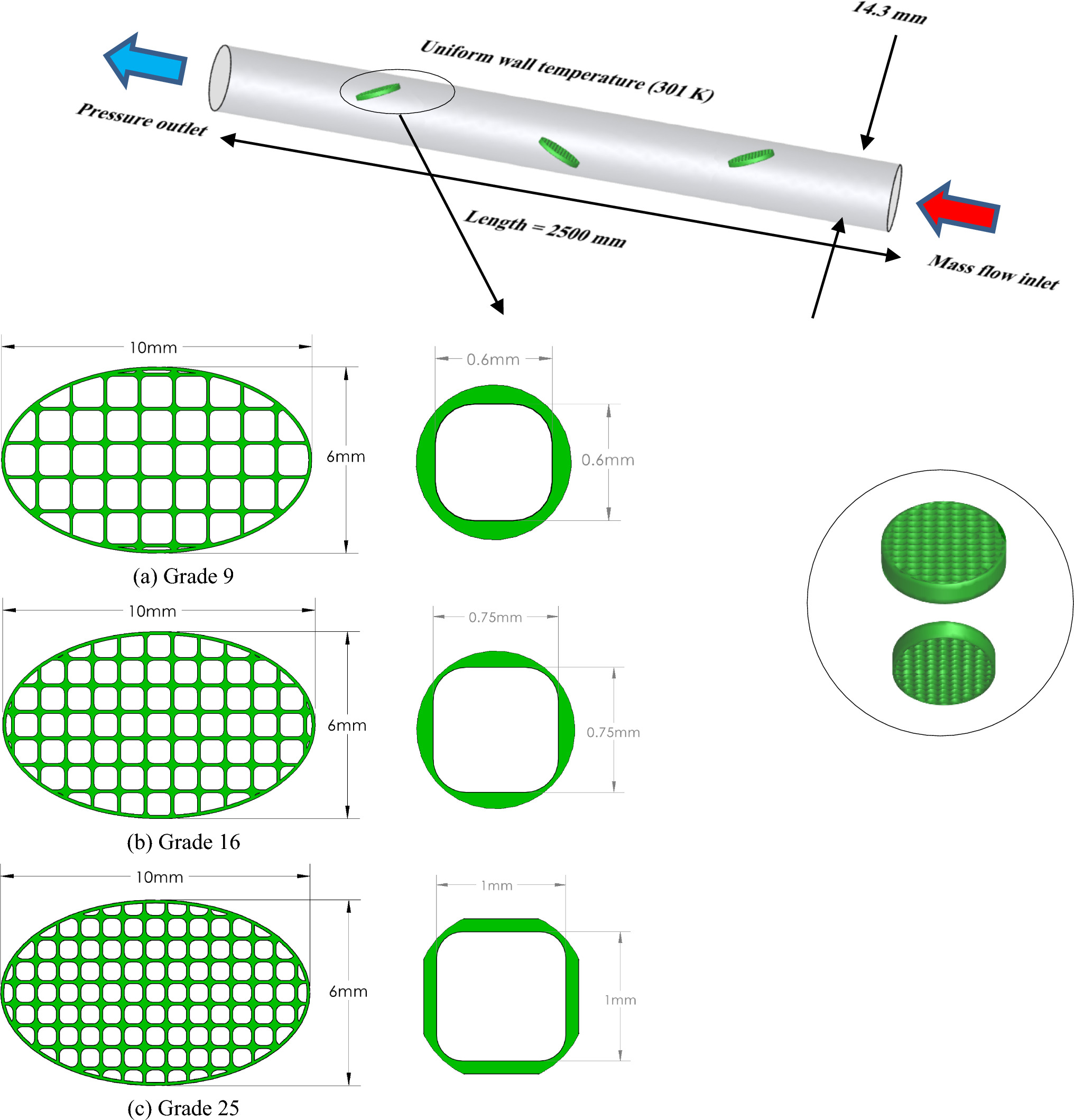
In the present study, the effect of a combination of rGO/Co3O4 nanofluid, with elliptical lattice turbulators on the flow parameters in a heat exchanger tube, was studied numerically. The aspects of energy consumption optimization in construction, design, and operation and the limitations of studies in the discussed area were the main motivations of the authors to do the present work. Elliptical lattice turbulators are installed in geometry in three grades (G = 9, 16, and 25). The angle of the turbulators with the horizontal axis is 25 degrees and the Re = 5000 to 18,000. The volume fraction of nanoparticles varies from 0 to 0.2%. The results showed that by adding nanoparticles to the base fluid, heat transfer increases and performance improves. The swirling flow inside the grids has a significant effect on improving excitation efficiency. The range of Nu 1.13–2.18, friction coefficient 1.30–2.95 times increases compared to the smooth pipe in all simulations. The highest thermal performance coefficient for the gridded oval is 25% higher than the normal oval ring at Re = 5000. The Nu by combining the use of turbulator and rGO/CO3O4 nanofluids in 0.2% compared to pure water in Re = 14,000 increases by 15.6%. Also, Nu and f increased by 189% and 174%, respectively. The highest thermal performance coefficient is 1.56 in Re = 5000 with φ = 0.2%.
All the authors have contributed equally to this work.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.