https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-04761-0
Regular Article
Predictive modeling of the heat of formation of sulfur hexafluoride using data science techniques
Department of Mathematics, COMSATS University Islamabad, Lahore Campus, Islamabad, Pakistan
Received:
21
July
2023
Accepted:
30
November
2023
Published online:
16
December
2023
Applications of graph theory exist in many science disciplines including chemistry, physics, medicine, and engineering. Since computational methods as well as computer-based approaches are less expensive and efficient, these techniques are very helpful to analyze chemical compounds. Chemical graph theory is a field that includes such kinds of analyses of chemical structures. Graph descriptors, also referred as topological indices, are graph invariants that help to study different structural properties of chemical substances. Such descriptors also aid to understand different activities related to chemical compounds. The main objective of this study is to find the best appropriate index to estimate the heat of formation of 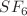 . Initially, we compute degree-based topological indices, co-indices, and reverse indices for Sulfur hexafluoride. A similarity measure is used for feature selection. A network of the indices is constructed based on a similarity measure which is defined using Euclidean distance and Pearson correlation. Next, twenty-one subnetworks of the network consisting of highly similar indices, referred as modules, are captured. One module is containing 13 indices, three are containing 2 indices, and all the remaining modules are comprised of only one vertex. Hierarchical clustering is used to verify the detected modules. From each module one index, called master regulatory index (
. Initially, we compute degree-based topological indices, co-indices, and reverse indices for Sulfur hexafluoride. A similarity measure is used for feature selection. A network of the indices is constructed based on a similarity measure which is defined using Euclidean distance and Pearson correlation. Next, twenty-one subnetworks of the network consisting of highly similar indices, referred as modules, are captured. One module is containing 13 indices, three are containing 2 indices, and all the remaining modules are comprised of only one vertex. Hierarchical clustering is used to verify the detected modules. From each module one index, called master regulatory index (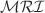 ), is selected for further study. Afterward, the thermodynamical measure heat of formation (
), is selected for further study. Afterward, the thermodynamical measure heat of formation (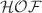 ) is computed. A correlation analysis is done between each master regulatory index and heat of formation to capture any uncorrelated feature, if exists. Finally, mathematical formulations between each
) is computed. A correlation analysis is done between each master regulatory index and heat of formation to capture any uncorrelated feature, if exists. Finally, mathematical formulations between each 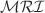 and
and 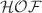 are estimated. The best estimate is selected based on root mean squared error.
are estimated. The best estimate is selected based on root mean squared error.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




