https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-04699-3
Regular Article
Bifurcation analysis of calcium dynamics in nerve cell
1
Indus University, Ahmedabad, India
2
Department of Mathematics, School of Technology, Pandit Deendayal Energy University, 382426, Gandhinagar, Gujarat, India
Received:
12
October
2023
Accepted:
10
November
2023
Published online:
30
December
2023
Communication between neurons and astrocytes involves numerous significant chemical transmissions. It has been established that 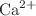 signaling is among the most adaptable second mediators in the majority of cell morphology and diverse cellular processes are regulated by complicated dynamical behaviors that range from random picking to well-ordered oscillations and periodic waves. Including muscular contraction, gene transcription, cell death, and neural activity. A significant regulator of intracellular
signaling is among the most adaptable second mediators in the majority of cell morphology and diverse cellular processes are regulated by complicated dynamical behaviors that range from random picking to well-ordered oscillations and periodic waves. Including muscular contraction, gene transcription, cell death, and neural activity. A significant regulator of intracellular 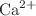 dynamics, including the voltage-gated
dynamics, including the voltage-gated 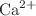 channels, the store-operated
channels, the store-operated 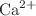 channel (SOCC), and the receptor-operated
channel (SOCC), and the receptor-operated 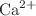 channel (ROCC), is the rate at which
channel (ROCC), is the rate at which 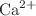 enters cells through plasma membrane cells. In order to analyze the model’s dynamic behavior, we have solved the neuron–astrocyte model and conducted a bifurcation analysis. The consequences of changing certain parameters, specifically the bifurcation of numerous limit cycles, on the dynamics of
enters cells through plasma membrane cells. In order to analyze the model’s dynamic behavior, we have solved the neuron–astrocyte model and conducted a bifurcation analysis. The consequences of changing certain parameters, specifically the bifurcation of numerous limit cycles, on the dynamics of 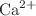 with changes in the signaling mechanism for distinct flows through the ER. Multiple limit cycle bifurcation, which may result in complicated dynamical behaviors, arises from the generalized coupling of mitochondria and NCX. It is further demonstrated that the parameter range for stable oscillations is determined by the fluctuation of the maximum flows for various calcium channels.
with changes in the signaling mechanism for distinct flows through the ER. Multiple limit cycle bifurcation, which may result in complicated dynamical behaviors, arises from the generalized coupling of mitochondria and NCX. It is further demonstrated that the parameter range for stable oscillations is determined by the fluctuation of the maximum flows for various calcium channels.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




