https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-04534-9
Regular Article
Travelling waves of a nonlinear reaction-diffusion model of the hepatitis B virus
1
Laboratory of Biophysics, Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, University of Yaounde I, P.O. Box 812, Yaounde, Cameroon
2
Department of Refining and Petrochemistry, National Advanced School of Mines and Petroleum Industries, University of Maroua, P.O. Box 46, Maroua, Cameroon
3
Department of Basic Scientific Teachings, National Advanced School of Engineering of Maroua, University of Maroua, P.O. Box 46, Maroua, Cameroon
4
Department of Mathematical and Statistical Sciences, Faculty of Natural and Agricultural Sciences, North-West University, 2735, Mafikeng, South Africa
Received:
29
March
2023
Accepted:
29
September
2023
Published online:
2
November
2023
A mathematical model of viral hepatitis B that takes into account healthy cells, infected cells and free viruses is studied in this paper. This model takes into account spatial mobility of all the three populations group mentioned and also drug treatment, the Rough-Hurwitz criteria are used to determine the stability conditions of this model. The traveling wave solutions are obtained by the exp(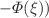 - expansion method in order to better appreciate the mechanism of infection by the hepatitis B virus and we obtain the bright, dark type profiles and show the effects of drug treatment on the amplitude of the solutions which, allows us to give more information on the treatment and control of the disease, we found that an increase in the dose of drug treatment promotes the development of healthy cells but that this increase significantly reduces the density of the viral population. Numerical simulations are carried out to verify the analytical predictions.
- expansion method in order to better appreciate the mechanism of infection by the hepatitis B virus and we obtain the bright, dark type profiles and show the effects of drug treatment on the amplitude of the solutions which, allows us to give more information on the treatment and control of the disease, we found that an increase in the dose of drug treatment promotes the development of healthy cells but that this increase significantly reduces the density of the viral population. Numerical simulations are carried out to verify the analytical predictions.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




