https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-04519-8
Regular Article
Influence of perturbations on linear and nonlinear optical properties of quantum dot
1
Institute of Engineering Mathematics,Universiti Malaysia Perlis, 02600, Arau, Perlis, Malaysia
2
Department of Physics, Cross River University of Technology, Calabar, Nigeria
3
Faculty of Electronic Engineering Technology, Universiti Malaysia Perlis, Kangar, Perlis, Malaysia
4
Physics Department, Faculty of Science, Sivas Cumhuriyet University, 58140, Sivas, Turkey
5
Department of Physics, National Open University of Nigeria, PMB 581, Jabi-Abuja, Nigeria
6
Advanced Communication Engineering (ACE) Centre of Excellence Universiti Malaysia Perlis, 01000, Kangar, Perlis, Malaysia
7
Institute of Nano Electronic Engineering (INEE), Universiti Malaysia Perlis (UniMAP), 01000, Kangar, Perlis, Malaysia
8
Geopolymer and Green Technology, Centre of Excellence (CEGeoGTech), Universiti Malaysia Perlis (UniMAP), Arau, Perlis, Malaysia
Received:
9
August
2023
Accepted:
24
September
2023
Published online:
10
October
2023
This study focused on investigating the influence of perturbations on the linear and nonlinear optical properties of 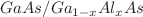 screened modified Kratzer potential (SMKP) quantum dot (QD). The optical absorption coefficients (OACs) and refractive index changes (RICs) for
screened modified Kratzer potential (SMKP) quantum dot (QD). The optical absorption coefficients (OACs) and refractive index changes (RICs) for 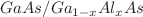 have been presented. The density matrix and iterative approaches were used to derive expressions of OACs and RICs in SMKP QD. The diagonalization method has been used to obtain energy eigenvalues and eigenfunctions of
have been presented. The density matrix and iterative approaches were used to derive expressions of OACs and RICs in SMKP QD. The diagonalization method has been used to obtain energy eigenvalues and eigenfunctions of 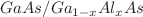 SMKP QD under the effects of Al concentration-x, hydrostatic pressure, and temperature. Our results reveal that the Al concentration-x, hydrostatic pressure, and temperature greatly impact the position and amplitude of the resonant peaks of the linear and nonlinear OACs and RICs. Interpretations have been presented in detail. The results of this study will find applications in the optical physics of semiconductors and other systems.
SMKP QD under the effects of Al concentration-x, hydrostatic pressure, and temperature. Our results reveal that the Al concentration-x, hydrostatic pressure, and temperature greatly impact the position and amplitude of the resonant peaks of the linear and nonlinear OACs and RICs. Interpretations have been presented in detail. The results of this study will find applications in the optical physics of semiconductors and other systems.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




