https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-04509-w
Regular Article
Impact of self-steepening and intra-pulse Raman scattering on modulation instability in multiple quantum wells
1
Department of Physics, Sarala Birla University, 835103, Ranchi, Jharkhand, India
2
Department of Physics, University of Science and Technology Meghalaya, 793101, Meghalaya, India
Received:
28
April
2023
Accepted:
21
September
2023
Published online:
28
September
2023
This paper presents the impact of self-steepening (SS) and intra-pulse Raman scattering (IRS) on stabilization of modulation instability of a continuous wave probe field in semiconductor double quantum wells under the mechanism of electromagnetically induced transparency, driven by a controlling field. By adjusting the control field and its related parameters, the linear absorption of the probe is comparatively reduced, and simultaneously, the nonlinear coefficient specifically Kerr nonlinearity is enhanced under the optically induced transparency. Due to the presence of SS, the instability gain and frequency bandwidth of gain are dramatically suppressed at higher values of probe peak power 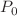 . Further, the combined effect of SS and IRS on instability gain enhances the number of frequency sidebands with the increase in
. Further, the combined effect of SS and IRS on instability gain enhances the number of frequency sidebands with the increase in 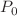 . The probe field can be stabilized against modulation instability, to an extent of desired frequency bandwidth by suitably selecting the SS and IRS, supported by control field Rabi frequency
. The probe field can be stabilized against modulation instability, to an extent of desired frequency bandwidth by suitably selecting the SS and IRS, supported by control field Rabi frequency 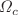 . The results of these investigation offer a novel method for the generation of solitonic or ultrashort optical pulses in the context of high-speed data transmission through optical media.
. The results of these investigation offer a novel method for the generation of solitonic or ultrashort optical pulses in the context of high-speed data transmission through optical media.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




