https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-04499-9
Regular Article
A study of novel molecular descriptors and quantitative structure–property relationship analysis of blood cancer drugs
1
Department of Mathematics, Division of Science and Technology, University of Education, Lahore, Pakistan
2
Department of Mathematics, University of Education Lahore, Vehari Campus, Lahore, Pakistan
3
Department of Mathematics and Statistics, University of Agriculture, 38000, Faisalabad, Pakistan
Received:
5
August
2023
Accepted:
13
September
2023
Published online:
27
September
2023
A molecular index is a numerical value derived from a chemical structure. Topological indices are used in quantitative structure-activity relationship studies to describe the symmetry of molecular structures and predict properties like boiling point, viscosity, spinning radius, melting point, flash point, and others. The abnormal cell growth that results in blood cancer is a serious disease. Several anti-cancer medications have been developed to reduce cell abnormalities. We use a theoretical way to explore the structure of anti-blood cancer drugs: graph invariants, also called molecular descriptors. In this article, the chemical structures of drugs used to treat blood cancer are examined using our new eight well-known degree-based topological indices, such as the reducible first and second Zagreb indices and the reducible Randic index. We try to estimate the boiling point, LogP, enthalpy, flash point, molar refractivity, molecular weight, and polarizability for blood cancer with the help of molecular descriptors. Newly introduced degree-based indices were assessed using QSPR analysis, employing linear, quadratic, and logarithmic models for 18 cancer drugs. In addition, the requirements of P-value 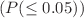 and F-test
and F-test 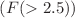 are also fulfilled by these models. The significance of the relationship between the experimental and estimated values describes the computation’s validity. To evaluate the model’s predictive power, we compare the predicted values of our model against the actual data values. It is clear that our model is reliable and can be used to make correct predictions for new data in the drug design field.
are also fulfilled by these models. The significance of the relationship between the experimental and estimated values describes the computation’s validity. To evaluate the model’s predictive power, we compare the predicted values of our model against the actual data values. It is clear that our model is reliable and can be used to make correct predictions for new data in the drug design field.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




