https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-04336-z
Regular Article
Horizontal stratification of fluids and the behavior of long waves
1
School of Medical Informatics and Engineering, Xuzhou Medical University, 209 Tongshan Road, 221004, Xuzhou, Jiangsu Province, People’s Republic of China
2
Department of Basic Science, Obour High Institute for Engineering and Technology, 11828, Cairo, Egypt
a mostafa.khater2024@yahoo.com, Mostafa.khater2024@xzhmu.edu.cn
Received:
28
May
2023
Accepted:
29
July
2023
Published online:
15
August
2023
This study employs contemporary and precise computational techniques to obtain innovative solitary wave solutions for the (3 + 1)-dimensional Kadomtsev-Petviashvili (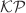 ) equation, which characterizes the behavior of long waves with small amplitudes compared to wavelengths in horizontally stratified fluids. The model accounts for nonlinearity, dispersion, and dissipation, all of which significantly influence wave propagation. The nonlinearity results in wave interactions and soliton formation, dispersion causes wave spreading over time, while dissipation represents energy loss. The generalized exponential function (
) equation, which characterizes the behavior of long waves with small amplitudes compared to wavelengths in horizontally stratified fluids. The model accounts for nonlinearity, dispersion, and dissipation, all of which significantly influence wave propagation. The nonlinearity results in wave interactions and soliton formation, dispersion causes wave spreading over time, while dissipation represents energy loss. The generalized exponential function ( ) method is utilized to construct solitary wave solutions, which are analyzed for their amplitude, width, and wave speed. The contribution of this study lies in enhancing the comprehension of physical phenomena dynamics, including surface waves in deep water, Langmuir waves in plasma physics, and electromagnetic waves in nonlinear optics. Comparisons with prior studies indicate the proposed technique’s reliability and accuracy in obtaining solitary wave solutions for the
) method is utilized to construct solitary wave solutions, which are analyzed for their amplitude, width, and wave speed. The contribution of this study lies in enhancing the comprehension of physical phenomena dynamics, including surface waves in deep water, Langmuir waves in plasma physics, and electromagnetic waves in nonlinear optics. Comparisons with prior studies indicate the proposed technique’s reliability and accuracy in obtaining solitary wave solutions for the 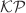 equation. Therefore, this study provides valuable insights into nonlinear science and has the potential to inform practical applications across various fields.
equation. Therefore, this study provides valuable insights into nonlinear science and has the potential to inform practical applications across various fields.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




