https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-04265-x
Regular Article
First-principles insights into the optical and electronic characteristics of barium intercalated AB-stacked bilayer graphene
1
Laboratoire de Physique des Matériaux et Modélisation des Systèmes, (LP2MS),Unité Associée au CNRST-URAC 08, Physics Department, Faculty of Sciences, University of Moulay Ismail, B.P. 11201, Meknes, Morocco
2
Condensed Matter Theory Group, Department of Physics and Astronomy, Uppsala University, 75120, Uppsala, Sweden
3
Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Technology Ropar, 140001, Rupnagar, Punjab, India
4
Grupo de Materia Condensada-UdeA, Instituto de Física, Facultad de Ciencias Exactas y Naturales, Universidad de Antioquia UdeA, Calle 70 No. 52-21, Medellín, Colombia
Received:
9
May
2023
Accepted:
7
July
2023
Published online:
11
August
2023
The present study describes the electronic and optical characteristics of barium atoms (an alkaline earth metal) intercalated within AB-stacked bilayer graphene (AB-2LG). Using state-of-the-art first-principles computations and taking into account the dispersion forces between the diverse nanosheets, we determined that the intercalation of barium atoms (Ba) into AB-2LG increases the interlayer distance from 3.357 to 5.584 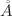 , and no C–Ba bond formation has been observed. In addition, our findings reveal that the presence of Ba atoms inside the AB-2LG induces a change in the Space group number from 164 (pure AB-2LG) to 156 (Ba-intercalated AB-2LG). Concurrently, we observed that the AB-2LG band structure exhibits a Dirac cone at the K-point, which is a characteristic signature of a semi-metallic character. By contrast, the electronic behavior of the barium-intercaled AB-2LG is found to be metallic. Also, we noticed that the confinement of Ba atoms into the AB-2LG shifts the Dirac point under the Fermi level. Additionally, upon examining the optical properties under the 001 and 100-polarization of the incident light, we found that all optical parameters of both under-investigated bidimensional materials exhibit an anisotropic character. Interestingly, under the 001-polarization, we observed that the intercalation of AB-2LG with Ba atoms reduces the optical absorption to zero in the visible region, and blueshifts are the absorption peak observed in the infrared region. Furthermore, in the case of 001-polarization, the presence of Ba atoms enhances the optical absorption in the 7–9 eV spectral range. However, the obtained data exhibit a remarkable decrease in the refractive index after the Ba intercalation process, for both considered polarization directions.
, and no C–Ba bond formation has been observed. In addition, our findings reveal that the presence of Ba atoms inside the AB-2LG induces a change in the Space group number from 164 (pure AB-2LG) to 156 (Ba-intercalated AB-2LG). Concurrently, we observed that the AB-2LG band structure exhibits a Dirac cone at the K-point, which is a characteristic signature of a semi-metallic character. By contrast, the electronic behavior of the barium-intercaled AB-2LG is found to be metallic. Also, we noticed that the confinement of Ba atoms into the AB-2LG shifts the Dirac point under the Fermi level. Additionally, upon examining the optical properties under the 001 and 100-polarization of the incident light, we found that all optical parameters of both under-investigated bidimensional materials exhibit an anisotropic character. Interestingly, under the 001-polarization, we observed that the intercalation of AB-2LG with Ba atoms reduces the optical absorption to zero in the visible region, and blueshifts are the absorption peak observed in the infrared region. Furthermore, in the case of 001-polarization, the presence of Ba atoms enhances the optical absorption in the 7–9 eV spectral range. However, the obtained data exhibit a remarkable decrease in the refractive index after the Ba intercalation process, for both considered polarization directions.
Supplementary Information The online version contains supplementary material available at https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-04265-x.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




