https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-04073-3
Regular Article
Accelerating universe via entropic models
Department of Mathematics, Quaid-i-Azam University, Islamabad, Pakistan
Received:
24
November
2022
Accepted:
27
April
2023
Published online:
23
May
2023
In this work, we propose new entropic force models by utilizing the non-extensive Tsallis entropy with a dimensionless parameter 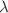 , which quantifies non-extensivity, and the Barrow entropy with quantum-gravitational deformation, which is quantified by a free parameter
, which quantifies non-extensivity, and the Barrow entropy with quantum-gravitational deformation, which is quantified by a free parameter 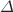 . We consider the universe as a sphere covered by the Hubble horizon. We have defined the Bekenstein entropy and Hawking temperature on the Hubble horizon by using the idea of Hawking and Bekenstein. We investigate the cosmological consequences of the proposed entropic force models and study the late time accelerating expansion of the universe. Although these models can describe the late time acceleration of the universe and the parameters
. We consider the universe as a sphere covered by the Hubble horizon. We have defined the Bekenstein entropy and Hawking temperature on the Hubble horizon by using the idea of Hawking and Bekenstein. We investigate the cosmological consequences of the proposed entropic force models and study the late time accelerating expansion of the universe. Although these models can describe the late time acceleration of the universe and the parameters 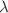 and
and 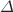 show satisfactory behavior by themselves. The parameter
show satisfactory behavior by themselves. The parameter 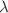 , and
, and 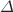 ranges
ranges 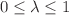 and
and 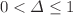 . This will be done by usnig the non-additive Tsallis entropy and Barrow entropy. In addition, the comparative analysis between Tsallis and Barrow for single-fluid dominated universe is also discussed. We investigate that the expansion of the universe is uniform as it was for the cases for Bekenstein and dark energy. Tsallis and Barrow entropy will be reduced to Bekenstein entropy for the certain limits of
. This will be done by usnig the non-additive Tsallis entropy and Barrow entropy. In addition, the comparative analysis between Tsallis and Barrow for single-fluid dominated universe is also discussed. We investigate that the expansion of the universe is uniform as it was for the cases for Bekenstein and dark energy. Tsallis and Barrow entropy will be reduced to Bekenstein entropy for the certain limits of 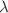 and
and 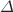 .
.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




