https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-022-03416-w
Regular Article
Geometrical scaling of heavy-quark contributions in the low x region
Department of Physics, Razi University, 67149, Kermanshah, Iran
Received:
30
June
2022
Accepted:
20
October
2022
Published online:
3
November
2022
We describe the determination of the heavy-quark structure functions 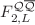 with help of the scaling properties. We observe that the structure functions for inclusive charm and bottom production exhibit geometric scaling at low x. The geometrical scaling means that the heavy-quark structure function is a function of only one dimensionless variable
with help of the scaling properties. We observe that the structure functions for inclusive charm and bottom production exhibit geometric scaling at low x. The geometrical scaling means that the heavy-quark structure function is a function of only one dimensionless variable 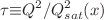 including quark mass. These results are valid for any value of
including quark mass. These results are valid for any value of 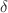 , being
, being 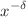 the behavior of the parton densities at low x. The determination of the heavy-quark structure function is presented as a parameterization of the proton structure function
the behavior of the parton densities at low x. The determination of the heavy-quark structure function is presented as a parameterization of the proton structure function 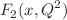 and its derivative. Analytical expressions for
and its derivative. Analytical expressions for 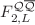 in terms of the effective parameters of the parameterization of
in terms of the effective parameters of the parameterization of 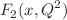 , with respect to the BDH and ASW models, are presented. To study the heavy-quark production processes, we use the collinear results in DAS approach. Numerical calculations and comparison with HERA data demonstrate that the suggested method provides reliable
, with respect to the BDH and ASW models, are presented. To study the heavy-quark production processes, we use the collinear results in DAS approach. Numerical calculations and comparison with HERA data demonstrate that the suggested method provides reliable 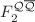 ,
, 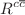 and
and 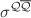 at low x in a wide range of the low absolute four-momentum transfers squared (
at low x in a wide range of the low absolute four-momentum transfers squared (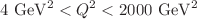 ). Also, in the HERA kinematic range, the ratio of
). Also, in the HERA kinematic range, the ratio of 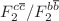 ,
, 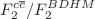 and
and 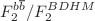 are obtained. Expanding the method to low and ultra-low values of x can be considered in the process analysis of the LHeC and FCC-eh colliders.
are obtained. Expanding the method to low and ultra-low values of x can be considered in the process analysis of the LHeC and FCC-eh colliders.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2022. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




