https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-022-02998-9
Regular Article
Ag@AgCl/Cu2+-Bi2O3 nanocomposite for decontamination of Rhodamine B: adsorption, kinetics, thermodynamics, and photocatalytic aspects
1
Department of Chemistry, Maharshi Dayanand University, 124001, Rohtak, India
2
Centre for Nanostructures and Advanced Materials, Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), 0001, Pretoria, South Africa
3
Department of Chemistry, University of the Western Cape, Robert Sobukwe Drive, Bag X17, 7535, Bellville, South Africa
4
Department of Chemistry, Baba Mastnath University, 124001, Rohtak, India
5
Department of Chemistry, Guru Jambheshwar University of Science & Technology, 125001, Hisar, India
g
naveenkumar.chem@mdurohtak.ac.in
Received:
29
April
2022
Accepted:
23
June
2022
Published online:
17
July
2022
A novel Ag@AgCl decorated Cu2+- Bi2O3 nanocomposite was successfully constructed by fastening Ag and AgCl nanocrystals onto the surface of Cu2+- Bi2O3 nanoparticles via the simple precipitation-deposition process. The synthesized products were characterized thoroughly by using different techniques; in terms of their structural features (XRD), morphological characteristics (SEM), constitutional elements (EDX and XPS), optical (UVDRS and PL), chemical bonding (FTIR), and photocatalytic properties. Highly crystalline and pure compounds were indicated by the XRD analysis. The SEM, EDX, and XPS analysis confirmed the flake-like morphology, high purity, and constitutional elements with their chemical states in the as-synthesized sample. The optical band gap energies (3.33–3.59 ev) were estimated with UV–Vis DRS analysis and PL spectra were recorded to analyze the fluorescence emission. The adsorption and catalytic performance of the prepared catalysts were tested for model organic pollutant RhB dye. Adsorption aspects were studied in terms of adsorption kinetic, isotherm, and thermodynamic models. Adsorption phenomenon was best explained by using the Langmuir isotherm (R2 = 0.997) and pseudo second-order kinetics models (R2 = 0.984). Moreover, in the thermodynamic parameters, negative values of  (− 61.13 kJ/mol) and
(− 61.13 kJ/mol) and 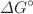 (− 0.619 kJ/mol) indicated exothermic and spontaneous adsorption, respectively at the lower temperatures. As photocatalyst, Ag@AgCl/Cu2+-Bi2O3 nanocomposites exhibited superior performance (99.60% degradation in 60
(− 0.619 kJ/mol) indicated exothermic and spontaneous adsorption, respectively at the lower temperatures. As photocatalyst, Ag@AgCl/Cu2+-Bi2O3 nanocomposites exhibited superior performance (99.60% degradation in 60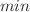 ) compared to the binary Cu2+-Bi2O3 sample (81.48%) for RhB removal. The role of
) compared to the binary Cu2+-Bi2O3 sample (81.48%) for RhB removal. The role of 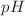 and active species involved in the degradation process were also analyzed.
and active species involved in the degradation process were also analyzed.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2022





