https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-022-02954-7
Regular Article
Control of non-Newtonian fluid flow and heat transfer in microchannel by using porous triangular ribs and pulsating jet
1
School of Mechanical Engineering, Arak University of Technology, Arak, Iran
2
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Technology Faculty, Fırat University, Elazig, Turkey
a
sdfarahani@arakut.ac.ir
d
hfoztop1@gmail.com
Received:
18
May
2022
Accepted:
14
June
2022
Published online:
27
June
2022
In this study, the numerical exploration of heat transfer of non-Newtonian fluid in a ribbed microchannel (MCH) with a pulsating impingement jet is inspected. The coolant is CMC-Water, which is a non-Newtonian fluid. The ribs are intended to be triangular with different angles as 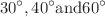 . The flow is two-dimensional laminar,
. The flow is two-dimensional laminar, 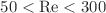 . The heat flux is applied to the lower wall of the microchannel. In the study, finite volume method is applied. The obtained results show that the heat transfer increases with increasing Re and decreasing rib angle. Among the four fins considered in the porous state, fin 1(near the MCH inlet) plays an imperative role in increasing heat transfer. Among the porous-nonporous fin arrangements, the state where all four fins are porous has the highest Nusselt number. Jet injection and increased injection velocity from the upper wall of the MCH have improved heat transfer. Jet slot 1 (located near the MCH entrance) has the most significant impact on the increase in heat transfer. When the jet is injected at an angle, in the single-jet mode, the minimum and maximum heat transfer are observed at an angle of
. The heat flux is applied to the lower wall of the microchannel. In the study, finite volume method is applied. The obtained results show that the heat transfer increases with increasing Re and decreasing rib angle. Among the four fins considered in the porous state, fin 1(near the MCH inlet) plays an imperative role in increasing heat transfer. Among the porous-nonporous fin arrangements, the state where all four fins are porous has the highest Nusselt number. Jet injection and increased injection velocity from the upper wall of the MCH have improved heat transfer. Jet slot 1 (located near the MCH entrance) has the most significant impact on the increase in heat transfer. When the jet is injected at an angle, in the single-jet mode, the minimum and maximum heat transfer are observed at an angle of 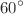 and
and 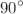 , respectively. Among the single-jet, two-jet, and four-jet modes, the best thermal performance has been reported for the four-jet mode with a
, respectively. Among the single-jet, two-jet, and four-jet modes, the best thermal performance has been reported for the four-jet mode with a 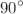 spray angle. The use of pulsating jets has a significant effect on improving heat transfer. Among the six combined modes of four pulsating jets (sine, constant and cosine), the highest heat transfer was reported for a pulsating jet with cosine velocity (mode 6).
spray angle. The use of pulsating jets has a significant effect on improving heat transfer. Among the six combined modes of four pulsating jets (sine, constant and cosine), the highest heat transfer was reported for a pulsating jet with cosine velocity (mode 6).
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2022




