https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-021-01239-9
Regular Article
New estimate of the chromomagnetic dipole moment of quarks in the standard model
1
Facultad de Ciencias Físico-Matemáticas, Benemérita Universidad Autónoma de Puebla, C.P. 72570, Puebla, Puebla, Mexico
2
Ingeniería en Mecatrónica, Universidad Politécnica de Puebla, Tercer Carril del Ejido Serrano s/n, San Mateo Cuanalá, Juan C. Bonilla, Puebla, Puebla, Mexico
Received:
24
September
2020
Accepted:
16
February
2021
Published online:
26
February
2021
A new estimate of the one loop contributions of the standard model to the chromomagnetic dipole moment (CMDM) 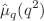 of quarks is presented with the aim to address a few disagreements arising in previous calculations. The most general case with arbitrary
of quarks is presented with the aim to address a few disagreements arising in previous calculations. The most general case with arbitrary 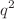 is considered and analytical results are obtained in terms of Feynman parameter integrals and Passarino-Veltman scalar functions, which are then expressed in terms of closed form functions when possible. It is found that while the QCD contribution to the static CMDM (
is considered and analytical results are obtained in terms of Feynman parameter integrals and Passarino-Veltman scalar functions, which are then expressed in terms of closed form functions when possible. It is found that while the QCD contribution to the static CMDM (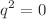 ) is infrared divergent, which agrees with previous evaluations and stems from the fact that this quantity has no sense in perturbative QCD, the off-shell CMDM (
) is infrared divergent, which agrees with previous evaluations and stems from the fact that this quantity has no sense in perturbative QCD, the off-shell CMDM (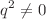 ) is finite and gauge independent, which is verified by performing the calculation for arbitrary gauge parameter
) is finite and gauge independent, which is verified by performing the calculation for arbitrary gauge parameter 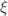 via both a renormalizable linear
via both a renormalizable linear 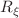 gauge and the background field method. It is thus argued that the off-shell
gauge and the background field method. It is thus argued that the off-shell 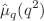 can represent a valid observable quantity. For the numerical analysis we consider the region 30 GeV
can represent a valid observable quantity. For the numerical analysis we consider the region 30 GeV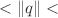 1000 GeV and analyze the behavior of
1000 GeV and analyze the behavior of 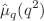 for all the standard model quarks. It is found that the CMDM of light quarks is considerably smaller than that of the top quark as it is directly proportional to the quark mass. In the considered energy interval, both the real and imaginary parts of
for all the standard model quarks. It is found that the CMDM of light quarks is considerably smaller than that of the top quark as it is directly proportional to the quark mass. In the considered energy interval, both the real and imaginary parts of 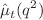 are of the order of
are of the order of  , with the largest contribution arising from the QCD induced diagrams, though around the threshold
, with the largest contribution arising from the QCD induced diagrams, though around the threshold 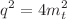 there are also important contributions from diagrams with Z gauge boson and Higgs boson exchange.
there are also important contributions from diagrams with Z gauge boson and Higgs boson exchange.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2021




