https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-020-00361-4
Regular Article
Big bang nucleosynthesis and entropy evolution in f(R, T) gravity
1
Department of Astronomy, Osmania University, Hyderabad, 500007, India
2
Department of Mathematics, Birla Institute of Technology and Science-Pilani, Hyderabad Campus, Hyderabad, 500078, India
* e-mail: pksahoo@hyderabad.bits-pilani.ac.in
Received:
13
January
2020
Accepted:
24
March
2020
Published online:
6
April
2020
The present article is devoted to constraining the model parameter 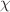 for the
for the 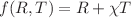 gravity model by employing the constraints coming from big bang nucleosynthesis. We solve the field equations and constrain
gravity model by employing the constraints coming from big bang nucleosynthesis. We solve the field equations and constrain 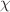 in the range
in the range 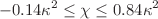 (where
(where 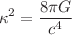 ) from the primordial abundances of light elements such as helium-4, deuterium and lithium-7. We found the abundances of helium-4 and deuterium agree with theoretical predictions; however, the lithium problem persists for the f(R, T) gravity model. We also investigate the evolution of entropy for the constrained parameter space of
) from the primordial abundances of light elements such as helium-4, deuterium and lithium-7. We found the abundances of helium-4 and deuterium agree with theoretical predictions; however, the lithium problem persists for the f(R, T) gravity model. We also investigate the evolution of entropy for the constrained parameter space of 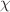 for the radiation and dust universe. We report that entropy is constant when
for the radiation and dust universe. We report that entropy is constant when 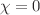 for the radiation-dominated universe, whereas for the dust universe, entropy increases with time. We finally use the constraints to show that
for the radiation-dominated universe, whereas for the dust universe, entropy increases with time. We finally use the constraints to show that 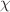 has a negligible influence on the cold dark matter annihilation cross section.
has a negligible influence on the cold dark matter annihilation cross section.
© Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature, 2020




