https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-020-00327-6
Regular Article
Modulated and enhanced magnetoelectric coupling in multiferroic [see pdf]
1
School of Physics and Electronics, North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power, Zhengzhou, 450045, China
2
Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures and Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructures, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210093, China
* e-mail: luoshijuncn@163.com
Received:
11
December
2019
Accepted:
11
March
2020
Published online:
2
April
2020
We investigate the effects of  doping on the magnetism, ferroelectricity, and magnetoelectric coupling in the
doping on the magnetism, ferroelectricity, and magnetoelectric coupling in the  . The lower Co doping (at
. The lower Co doping (at 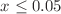 ) suppresses the commensurate collinear antiferromagnetic phase (AF1 phase) and stabilizes the ferroelectric phase down to
) suppresses the commensurate collinear antiferromagnetic phase (AF1 phase) and stabilizes the ferroelectric phase down to  . For higher Co substitution levels
. For higher Co substitution levels 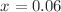 and 0.07, the ferroelectric polarization P reaches a peak at
and 0.07, the ferroelectric polarization P reaches a peak at  and
and  , respectively, and decreases to nonzero (measured at
, respectively, and decreases to nonzero (measured at  ) with further cooling, which can be attributed into a continuous rotation of the spiral plane driven by the small change in temperature. The polarization P at
) with further cooling, which can be attributed into a continuous rotation of the spiral plane driven by the small change in temperature. The polarization P at 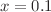 increases monotonically with cooling, which suggests the orientation of the spin helix unchanged. Ferroelectric polarization P reverses synchronously with the applying the cyclic oscillation external magnetic field and suggests that the polarization P is strongly coupled with the magnetism in the
increases monotonically with cooling, which suggests the orientation of the spin helix unchanged. Ferroelectric polarization P reverses synchronously with the applying the cyclic oscillation external magnetic field and suggests that the polarization P is strongly coupled with the magnetism in the  sample.
sample.
© Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature, 2020




