https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2018-12177-8
Regular Article
Raman spectroscopy and optical properties of GAZO thin films deposited at various substrate temperatures
1
Department of Physics and Astronomy, Botswana International University of Science and Technology (BIUST), P. Bag 16, Palapye, Botswana
2
Department of Physics and Mathematics, Bindura University of Science Education (BUSE), P. Bag 1020, Bindura, Zimbabwe
* e-mail: muchuweniedigar1@gmail.com
Received:
28
March
2018
Accepted:
7
July
2018
Published online:
17
August
2018
We report the Raman study and optical properties of gallium and aluminium co-doped ZnO (GAZO) thin films deposited at various substrate temperatures by sputtering. The films exhibited Raman peaks at 99 cm-1, 437 cm-1 and 575 cm-1 which were assigned to the ZnO  (low),
(low),  (high) and
(high) and 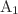 (LO) modes, respectively. The wavelength dependence of the refractive index and the extinction coefficient were described by the Cauchy dispersion model, through theoretical modelling of the transmittance data. The refractive index showed an increasing trend while the extinction coefficient decreased with increasing substrate temperature in the visible region. This was attributed to the relative decrease in transmittance observed at higher substrate temperatures. The dielectric constant (
(LO) modes, respectively. The wavelength dependence of the refractive index and the extinction coefficient were described by the Cauchy dispersion model, through theoretical modelling of the transmittance data. The refractive index showed an increasing trend while the extinction coefficient decreased with increasing substrate temperature in the visible region. This was attributed to the relative decrease in transmittance observed at higher substrate temperatures. The dielectric constant ( ) , dissipation factor
) , dissipation factor  and optical conductivity (
and optical conductivity ( ) values were associated with the films’ high transparency. The Wemple and Didomenico single oscillator dispersion energies (
) values were associated with the films’ high transparency. The Wemple and Didomenico single oscillator dispersion energies (  and
and  increased with substrate temperature which was attributed to the reduction in residual stress, improvement in microstructural order and crystallinity. The static refractive index
increased with substrate temperature which was attributed to the reduction in residual stress, improvement in microstructural order and crystallinity. The static refractive index  , optical band gap
, optical band gap  , long wavelength dielectric constant (
, long wavelength dielectric constant (  , the
, the  and
and  moments of the optical spectra and the non-linear refractive index (
moments of the optical spectra and the non-linear refractive index (  were determined. Optimum optical properties were obtained in films deposited on heated substrates (75 and
were determined. Optimum optical properties were obtained in films deposited on heated substrates (75 and 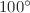 C).
C).
© Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature, 2018







