https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2018-12158-y
Regular Article
Thermodynamic and thermoeconomic optimization of coupled thermal and chemical engines by means of an equivalent array of uncoupled endoreversible engines
1
Escuela Superior de Física y Matemáticas del Instituto Politécnico Nacional, Edif. 9, UP Zacatenco, CP 07738, Mexico City, Mexico
2
Escuela Superior de Cómputo del Instituto Politécnico Nacional, Av. Juan de Dios Bátiz s/n UP Zacatenco, CP 07738, Mexico City, Mexico
* e-mail: mbarrancoj@ipn.mx
Received:
30
May
2018
Accepted:
13
July
2018
Published online:
29
August
2018
In 1994, De Mey and De Vos (MV) proposed an analysis of an array of two endoreversible heat engines connected by a thermal bridge. Their objective was to show that the well-known Curzon-Ahlborn (CA) efficiency,  , is not a universal value for endoreversible engines with a Newtonian heat transfer law. MV found that the efficiency of such an array performing at maximum power is given by
, is not a universal value for endoreversible engines with a Newtonian heat transfer law. MV found that the efficiency of such an array performing at maximum power is given by 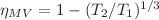 . However, we show that the CA formula also is present in the MV array when it performs at maximum efficiency. In the present work we made both thermodynamic and thermoeconomic analyses of the MV model and we show an equivalent array formed by three uncoupled endoreversible engines operating simultaneously between the same thermal reservoirs. We extend all the previous analyses to the case of a chemical MV-type array. In all cases three objective functions were used: maximum power, maximum ecological function and maximum efficiency.
. However, we show that the CA formula also is present in the MV array when it performs at maximum efficiency. In the present work we made both thermodynamic and thermoeconomic analyses of the MV model and we show an equivalent array formed by three uncoupled endoreversible engines operating simultaneously between the same thermal reservoirs. We extend all the previous analyses to the case of a chemical MV-type array. In all cases three objective functions were used: maximum power, maximum ecological function and maximum efficiency.
© Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature, 2018




