https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2018-11865-7
Regular Article
Turbophoresis in forced inhomogeneous turbulence
1
Nordita, KTH Royal Institute of Technology and Stockholm University, Roslagstullsbacken 23, 10691, Stockholm, Sweden
2
Department of Energy and Process Engineering, NTNU, 7491, Trondheim, Norway
3
SINTEF Energy Research, 7465, Trondheim, Norway
4
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, POB 653, 84105, Beer-Sheva, Israel
* e-mail: dhruba.mitra@gmail.com
Received:
1
October
2017
Accepted:
9
January
2018
Published online:
5
February
2018
We show, by direct numerical simulations, that heavy inertial particles (characterized by Stokes number St) in inhomogeneously forced statistically stationary isothermal turbulent flows cluster at the minima of mean-square turbulent velocity. Two turbulent transport processes, turbophoresis and turbulent diffusion together determine the spatial distribution of the particles. If the turbulent diffusivity is assumed to scale with turbulent root-mean-square velocity, as is the case for homogeneous turbulence, the turbophoretic coefficient can be calculated. Indeed, for the above assumption, the non-dimensional product of the turbophoretic coefficient and the rms velocity is shown to increase with St for small St, reach a maxima for 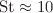 and decrease as
and decrease as 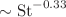 for large St.
for large St.
© The Author(s), 2018




