https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2017-11660-0
Regular Article
Numerical analysis of 3D micropolar nanofluid flow induced by an exponentially stretching surface embedded in a porous medium
Department of Mathematics, Quaid-i-Azam University, 44000, Islamabad, Pakistan
* e-mail: msubhani@math.qau.edu.pk
Received:
3
July
2017
Accepted:
24
August
2017
Published online:
27
October
2017
The present article is devoted to probe the behavior of a three-dimensional micropolar nanofluid over an exponentially stretching surface in a porous medium. The mathematical model is constructed in the form of partial differential equations using the boundary layer approach. Then by employing similarity transformations, the modelled partial differential equations are transformed to ordinary differential equations. The solution of subsequent ODEs is derived by utilizing the BVP-4C technique alongside the shooting scheme. The graphical illustrations are presented to interpret the salient features of pertinent physical parameters on the concerned profiles for different kinds of nanoparticles, namely copper, titania and alumina with water as the base fluid. For a better understanding of the fluid flow, the numerical variation in the local skin friction coefficients, 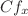 and
and  , and local Nusselt number is analyzed through tables. We can see, from the present study, that the omission of porous matrix enhances the flow of the fluid. Microrotation has a decreasing impact on the skin friction whereas it increases the rate of the heat transfer of the nanofluid.
, and local Nusselt number is analyzed through tables. We can see, from the present study, that the omission of porous matrix enhances the flow of the fluid. Microrotation has a decreasing impact on the skin friction whereas it increases the rate of the heat transfer of the nanofluid.
© Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, 2017




