https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2017-11584-7
Regular Article
A comparative ab intio study on structural evolution, stability and electronic properties of undoped and Al-doped GaxNy ( x + y = 4-25 clusters
Department of Applied Physics, Babasaheb Bhimrao Ambedkar University, 226025, U.P., Lucknow, India
* e-mail: akyadavbbau@gmail.com
Received:
19
March
2017
Accepted:
3
June
2017
Published online:
20
July
2017
We present a comparative study on structure evolution, binding energies, relative stabilities, electronic and vibrational properties of size-selected GaN and Al-doped GaN clusters by employing B3LYP exchange-correlation function with double-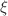 basis set LANL2DZ via the density functional theory (DFT) method. Cube, ring, and rhombus stacks are constructed, and the optimization results suggest that the evolution of basic structural entities of different morphologies from planer rings to nanotubes may be realized by taking into account the stacking mode of stable clusters. We also find that the geometry of each Al-substituted GaN cluster keeps a structure similar to that of the corresponding pure GaN clusters. The stability, IR and Raman activity vary with the growth of units and the stacking mode. The energetic analysis shows that the most stable structure is the 3-dimensional cubic structure. A blue shift in the vibrational frequency of the most intense Raman activity has been observed with variation in size and structure. Moreover, the vibrational properties are significantly affected by the introduction of Al dopants. We also consider parameters, such as HOMO-LUMO gap, ionization potential (IP), electron affinity (EA), dipole moment (DM), chemical potential (CP), chemical hardness (CH), and results were compared and critically discussed for interpretation of the enhanced stability and to extract useful information for their applications.
basis set LANL2DZ via the density functional theory (DFT) method. Cube, ring, and rhombus stacks are constructed, and the optimization results suggest that the evolution of basic structural entities of different morphologies from planer rings to nanotubes may be realized by taking into account the stacking mode of stable clusters. We also find that the geometry of each Al-substituted GaN cluster keeps a structure similar to that of the corresponding pure GaN clusters. The stability, IR and Raman activity vary with the growth of units and the stacking mode. The energetic analysis shows that the most stable structure is the 3-dimensional cubic structure. A blue shift in the vibrational frequency of the most intense Raman activity has been observed with variation in size and structure. Moreover, the vibrational properties are significantly affected by the introduction of Al dopants. We also consider parameters, such as HOMO-LUMO gap, ionization potential (IP), electron affinity (EA), dipole moment (DM), chemical potential (CP), chemical hardness (CH), and results were compared and critically discussed for interpretation of the enhanced stability and to extract useful information for their applications.
© Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, 2017




