https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2017-11390-3
Regular Article
Median statistics estimates of Hubble and Newton's constants
Department of Physics, IIT Hyderabad, 502285, Telangana, India
* e-mail: shntn05@gmail.com
Received:
4
November
2016
Accepted:
6
January
2017
Published online:
16
February
2017
Robustness of any statistics depends upon the number of assumptions it makes about the measured data. We point out the advantages of median statistics using toy numerical experiments and demonstrate its robustness, when the number of assumptions we can make about the data are limited. We then apply the median statistics technique to obtain estimates of two constants of nature, Hubble constant (H0) and Newton's gravitational constant (G , both of which show significant differences between different measurements. For H0, we update the analyses done by Chen and Ratra (2011) and Gott et al. (2001) using 576 measurements. We find after grouping the different results according to their primary type of measurement, the median estimates are given by 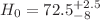 km/sec/Mpc with errors corresponding to 95% c.l. (2
km/sec/Mpc with errors corresponding to 95% c.l. (2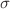 ) and
) and 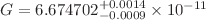 Nm2kg-2 corresponding to 68% c.l. (1
Nm2kg-2 corresponding to 68% c.l. (1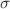 ).
).
© Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, 2017




